















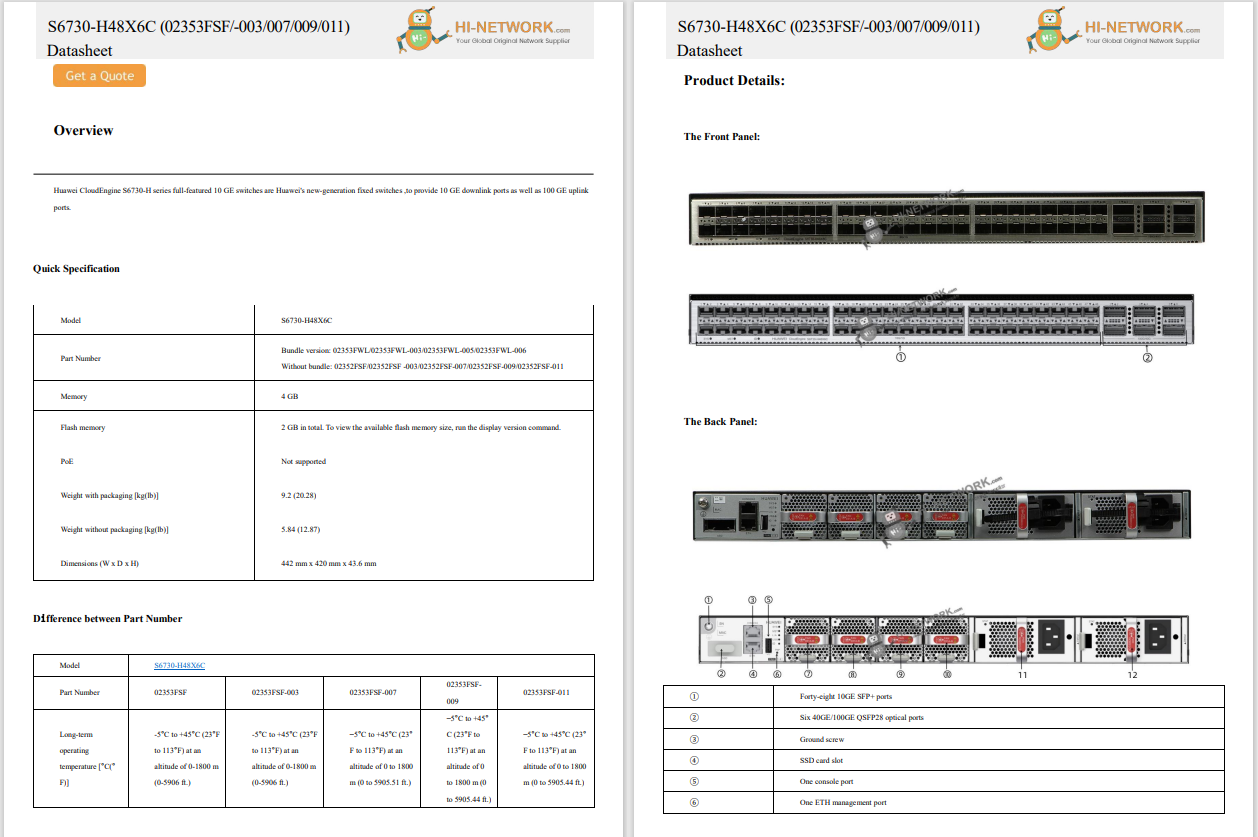










We are aware that there are seven systems in integrated wiring. So, what are the purposes and roles of these seven systems? Where are they located? In this article, we will provide a detailed explanation.
The seven subsystems of network integrated wiring are as follows:
1. Workspace Subsystem: This subsystem is responsible for providing wiring connections within individual workspaces.
2. Horizontal Subsystem: The horizontal subsystem is in charge of connecting the workspace subsystem to the vertical subsystem.
3. Vertical Subsystem: The vertical subsystem connects the horizontal subsystem to the equipment room subsystem.
4. Inter-management subsystem: This subsystem handles the management and coordination of the other subsystems.
5. Equipment room subsystem: The equipment room subsystem houses the necessary equipment for network connectivity.
6. Incoming wire room subsystem: This subsystem manages the incoming wires that connect to the building's network.
7. Building group subsystem: The building group subsystem oversees the integration of all the subsystems within the building.
These seven systems are interconnected and each one plays a crucial role. Let's explore their functions together.
1. Workspace subsystem: used by front-end users
Workspace subsystem, which is also known as the service area subsystem, is utilized by users in the front-end. It comprises of terminal equipment like jumpers and information sockets. The main components consist of information panels, information modules, terminal jumpers, and home wiring information boxes. It serves as a user-friendly interface for individuals to use in their offices.
When installing, please take note of the following:
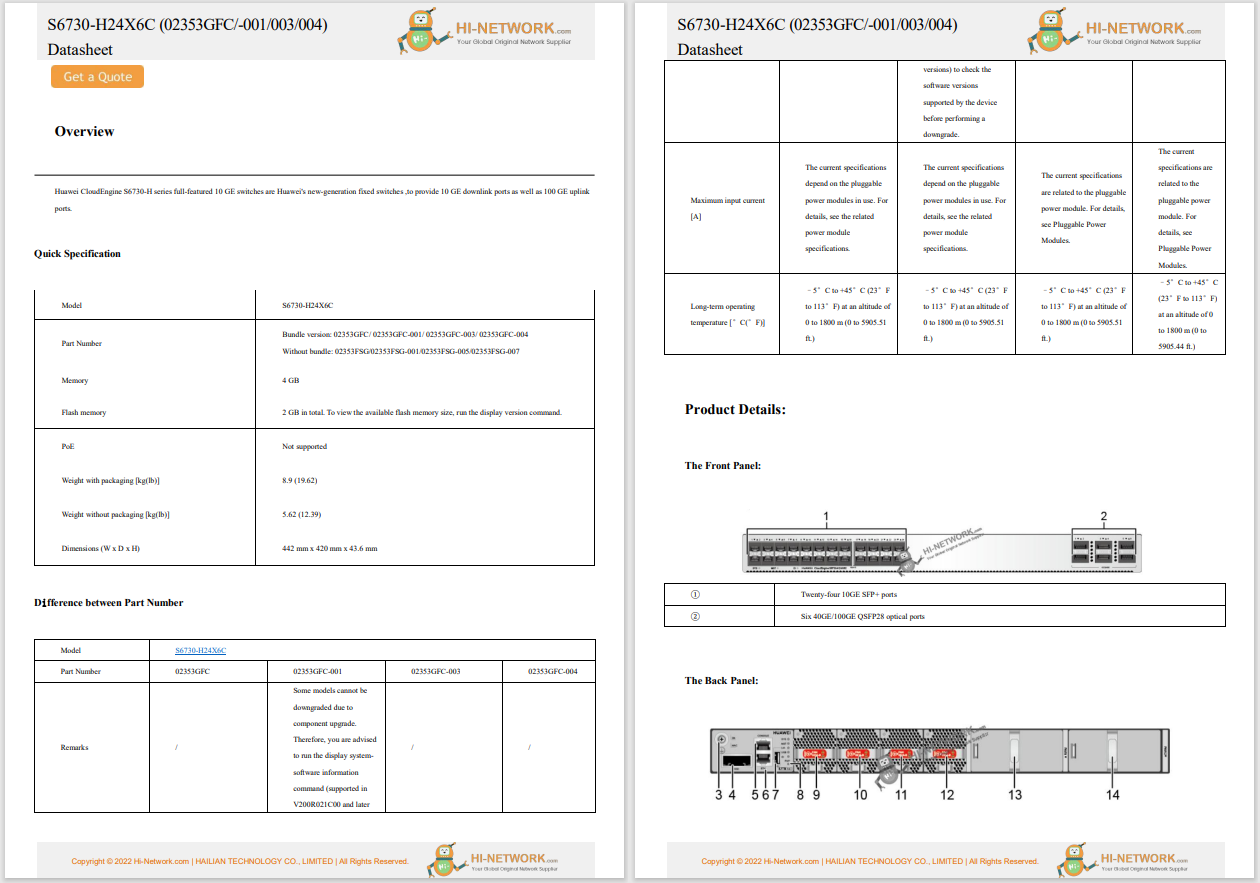
1. The connection between the RJ45 socket and the terminal equipment should be made using a twisted pair, with a maximum length of five meters.
2. The RJ45 socket should ideally be installed on a wall that is not easily accessible.
3. There should be a minimum distance of 20cm between the RJ45 socket and the power socket.
4. For wall-mounted information sockets and power sockets, the bottom surface should be positioned 30cm above the ground.
2. Horizontal Subsystem: Information Points
The horizontal subsystem refers to the distribution room on the floor that connects to the user's information socket in the work area. The main component of this subsystem is the horizontal network cable, and the fiber-to-the-home system also includes horizontal optical cables. Each information point needs to be connected to the management subsystem, which can be thought of as a horizontal information point, as shown in the figure below.
When installing, please keep in mind the following points:
1. Decide on the wiring method and the direction of the cable.
2. The length of the twisted pair should not exceed 90 meters.
3. Avoid running long horizontal cables parallel to power supply lines. There should be a minimum distance between them. Generally, for unshielded cables, the distance is 30 centimeters, and for shielded cables, it is 7 centimeters.
4. The cables should be routed through wire troughs or in the ceiling.
5. If the wiring needs protection in a specific environment, use metal pipes or similar measures.
6. Determine the distance between the management room and the nearest and farthest terminals.
3. Vertical Trunk Subsystem: Providing Connections
The vertical trunk subsystem consists of cables that connect the main equipment room to the distribution rooms on each floor. Its main function is to connect each level of distribution frame to the main distribution frame. Backbone cables are used to create communication channels between floors, making the entire wiring system a unified whole. The main products used are Asia-Pacific optical cables, large logarithmic cables, and telephone cables.
4. Management Subsystem: Intermediary Station
The management room subsystem, also known as the wiring room or wire room, is where distribution frames, floor cabinets, and switches are installed to connect the vertical subsystems and horizontal trunk subsystems. In practical projects, it is typically a weak electrical well located between buildings. It acts as an intermediary station, providing a connection point for back-end management and front-end users.
5. Equipment Room Subsystem: Back-End Computer Room
The equipment room subsystem, also known as the network intermediate computer room, consists of cables and related hardware that enable network management and information exchange at specific points within the building. The main equipment includes computer network equipment, servers, firewalls, routers, program-controlled switches, and building switching equipment hosts.
6. Incoming Line Room Subsystem: Pipeline Entrance between Equipment Room and Building
The incoming line room serves as the entrance for external communication and information pipelines of the building, connecting the subsystems of the equipment room with the building group subsystems. The incoming line room is typically accessed through buried pipelines during the construction phase.
7. Building Complex Subsystem: Communication Linking Multiple Buildings
The building complex subsystem is used when there is a need for voice, data, and image connections among buildings such as schools, troops, government agencies, and communities. It consists of data, telephone, and video system cables that connect two or more buildings. The main products used are outdoor optical cables, outdoor large logarithmic cables, and telephone cables. It enables communication between buildings.
These seven subsystems make up the integrated wiring system, facilitating communication, management, and connectivity between buildings.
Interested in learning more about network cabling and IT equipment? Visit our website, Hi-Network! Here, you'll find high-quality products and professional solutions to meet all your IT needs. Click the link now to explore more exciting content and purchase the products you require!
Check More Hi-Network Products:
 Hot Tags :
network
Hot Tags :
network