













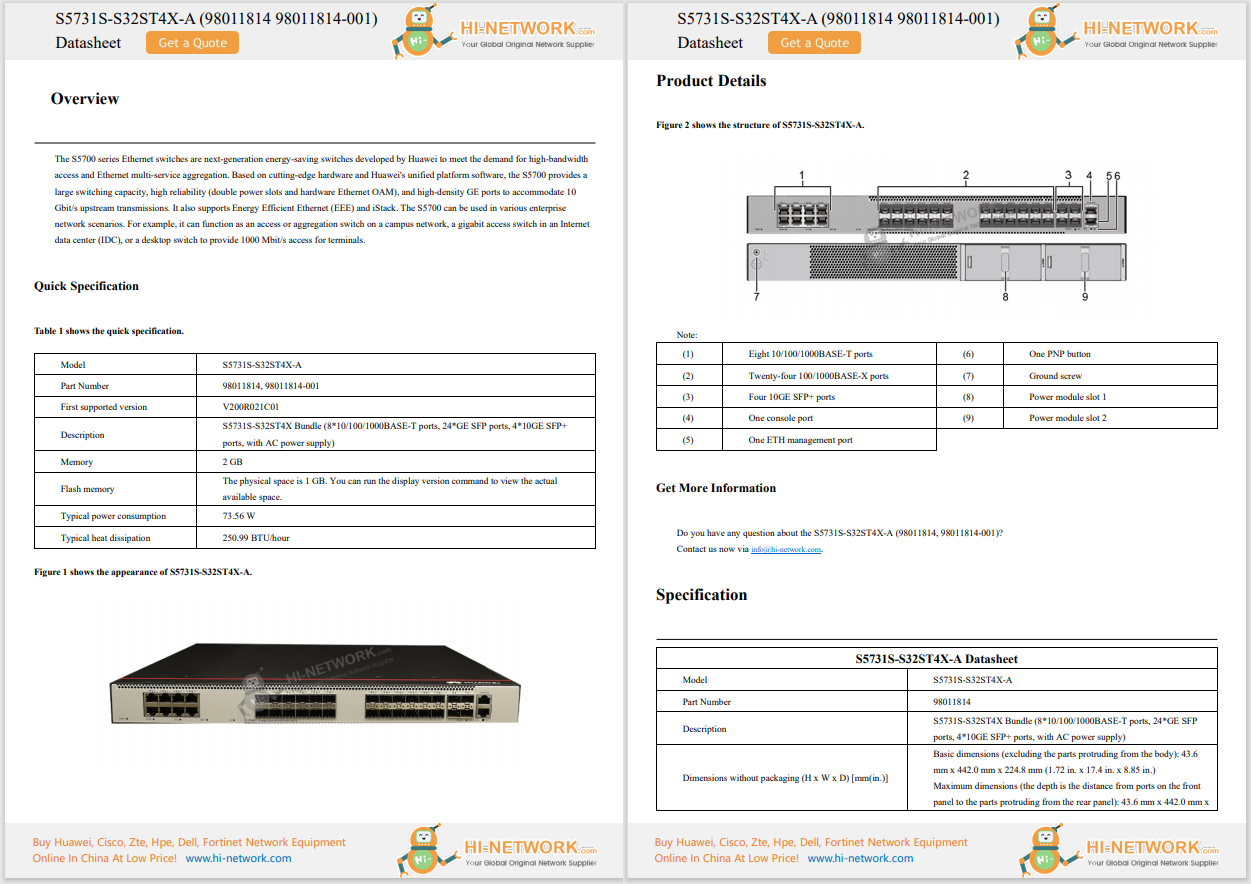













This article aims to provide a clear explanation of what IP routing is and how it functions. So, continue reading to gain a better understanding.
IP routing refers to the process of forwarding packets from one network to another, often traversing multiple networks before reaching the intended destination. It operates by utilizing different internet protocol technologies and routing tables, which work together to determine the most optimal path for the data to travel.
During my studies to become a network engineer, I always found it challenging to comprehend the purpose and workings of IP routing. However, I have since gained a better understanding, and I believe many others may still struggle with it. Therefore, I have written this article to provide a clear explanation of what IP routing is and how it functions. So, continue reading to learn more.
What is IP Routing
IP Routing is a technology that determines the route for data packets between networks. It moves data from a source to its intended destination by passing it through different networks. These networks receive and pass on the packets to the next network. This is done by a network router, which examines the destination and selects the best path for the data packets.
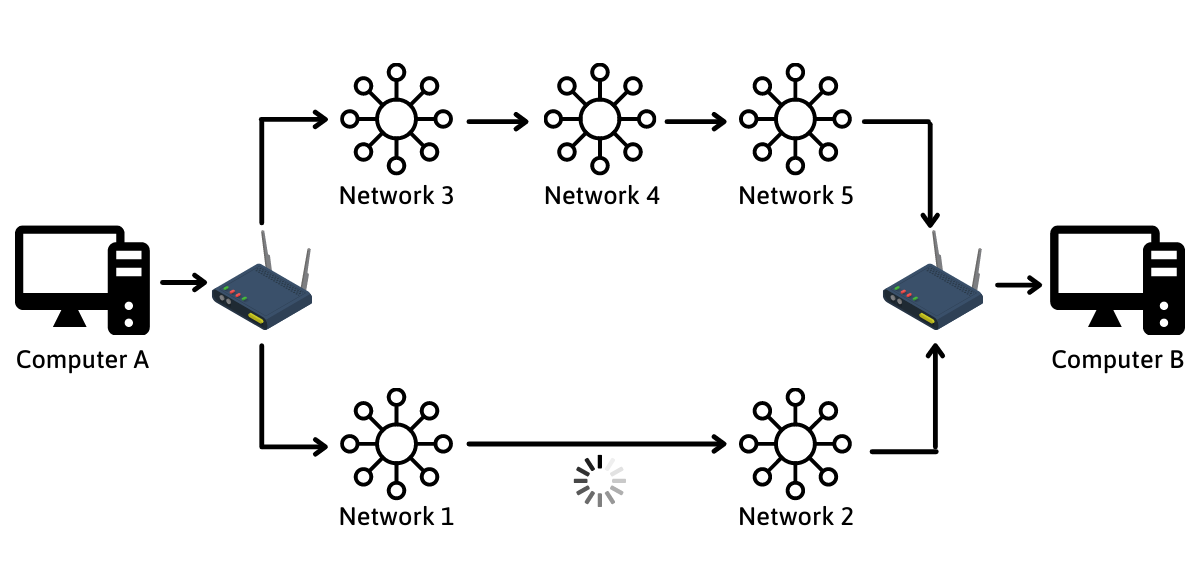
In the example shown below, you can see how routing works. Computer A wants to send data to Computer B. Initially, Computer A sends the data to its router. The router then determines the most efficient path for the data.
In this case, the router identifies two possible paths. The first and shortest path goes through Network 1 and 2. The second, longer path goes through Network 3, 4, and 5. It would be an easy decision if all the networks had the same speed, but Network 3, 4, and 5 have a faster speed compared to Network 1 and 2. Therefore, the router must decide which route is the fastest.
How Does IP Routing Work
When a router receives a packet, whether it's from its own computer or another router, it reads the packet's headers to find out where it is supposed to go. Once it knows the destination of the packet, it uses a routing table to determine the best path for the packet to take.
You can think of a routing table as a schedule for trains. Just like passengers look at the schedule to decide which train to take, routers use routing tables to decide which network path to choose. However, unlike passengers who can make their own decisions, packets rely on the router to tell them which path to take, just like passengers would ask train station personnel for directions.
There are two main types of routing tables that routers can use: static routing tables and dynamic routing tables.
Static Routing Tables
A static routing table is created by the network administrator through manual setup. It requires configuration on each router to ensure smooth operation. The table remains unchanged unless the administrator modifies it. Now, let's discuss the pros and cons of static routing tables.
ADVANTAGES
Simple to set up and handle on small networks
It provides enhanced security as there is no need to analyze routing protocols.
Simple to configure on smaller networks within a larger network
Requires less computer resources (CPU, memory, bandwidth)
DISADVANTAGES
It is extremely challenging to handle and control larger networks.
They do not prevent the occurrence of routing loops.
Whenever there are any modifications, the administrator needs to manually update the routers.
There is no automatic redirection of traffic if there is a network outage.
Dynamic Routing Tables
Routers can create dynamic routing tables on their own without any manual intervention. Whenever there is a change in the network, these tables are automatically updated. These smart routing protocols have the ability to select a new path when there is a change in the routing or network structure. Let's discuss the pros and cons of dynamic routing tables.
ADVANTAGES
No need to manually set up or manage the router.
Simple to manage on a bigger network.
Avoid routing mistakes.
Automatically include new routes.
Effortless to expand.
DISADVANTAGES
Requires higher computer processing capabilities (CPU), more memory, and greater bandwidth.
Demands a more intricate initial setup for proper functioning.
Routing Protocols
Routers have various routing protocols at their disposal to determine the most efficient path. However, they often utilize multiple protocols simultaneously to determine the optimal route for data transmission. Here are some of the most frequently used ones:
BGP
BGP is short for Border Gateway Protocol. Its main purpose is to determine which network has which IP address and which networks are connected to each other. BGP is a kind of dynamic routing protocol and it functions smoothly with dynamic routing tables.
OSPF
OSPF is an acronym for Open Shortest Path First. Routers utilize it to discover the quickest and most direct path for packets to reach their intended destination.
RIP
RIP is short for Routing Information Protocol and it uses the number of routers that a packet passes through to determine the shortest route to its destination. Hop counts refer to the number of routers that need to receive and forward the packet from the sender to its destination. RIP always aims to find the route with the least number of hops, even if it's not necessarily the fastest route.
EIGRP
EIGRP is an acronym for Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol, which is a highly developed routing protocol based on distance-vector technology. Its main purpose is to automate the process of making routing decisions and setting up configurations.
IS-IS
IS-IS is an acronym for Intermediate System – Intermediate System and is a different kind of IP routing protocol. It is quite similar to OSPF, with the main distinction being that OSPF works at layer 1, whereas IS-IS operates at layer 2.
Bottom Line
IP Routing is the process that helps packets travel across networks and is the basic principle behind the internet. Routers use different internet protocols and routing tables to direct the data and find the best route for the packets. Various methods are employed for networks of different sizes and locations. However, the ultimate goal remains unchanged: to ensure smooth and effective communication between networks.
If you need Switches, Routers, or need more network information, welcome to contact us www.hi-network.com (Email: info@hi-network.com)
 Hot Tags :
network
ROUTERS
Hot Tags :
network
ROUTERS