














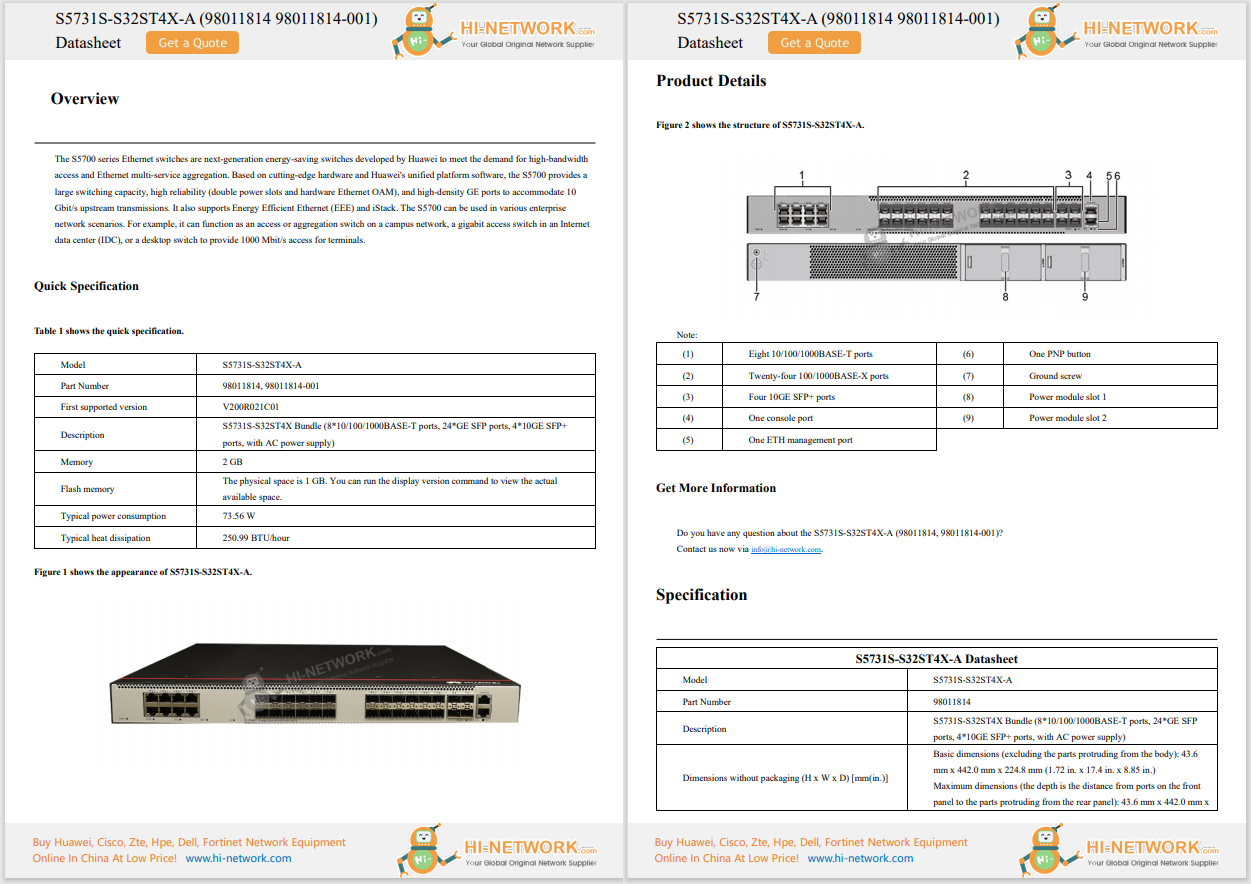











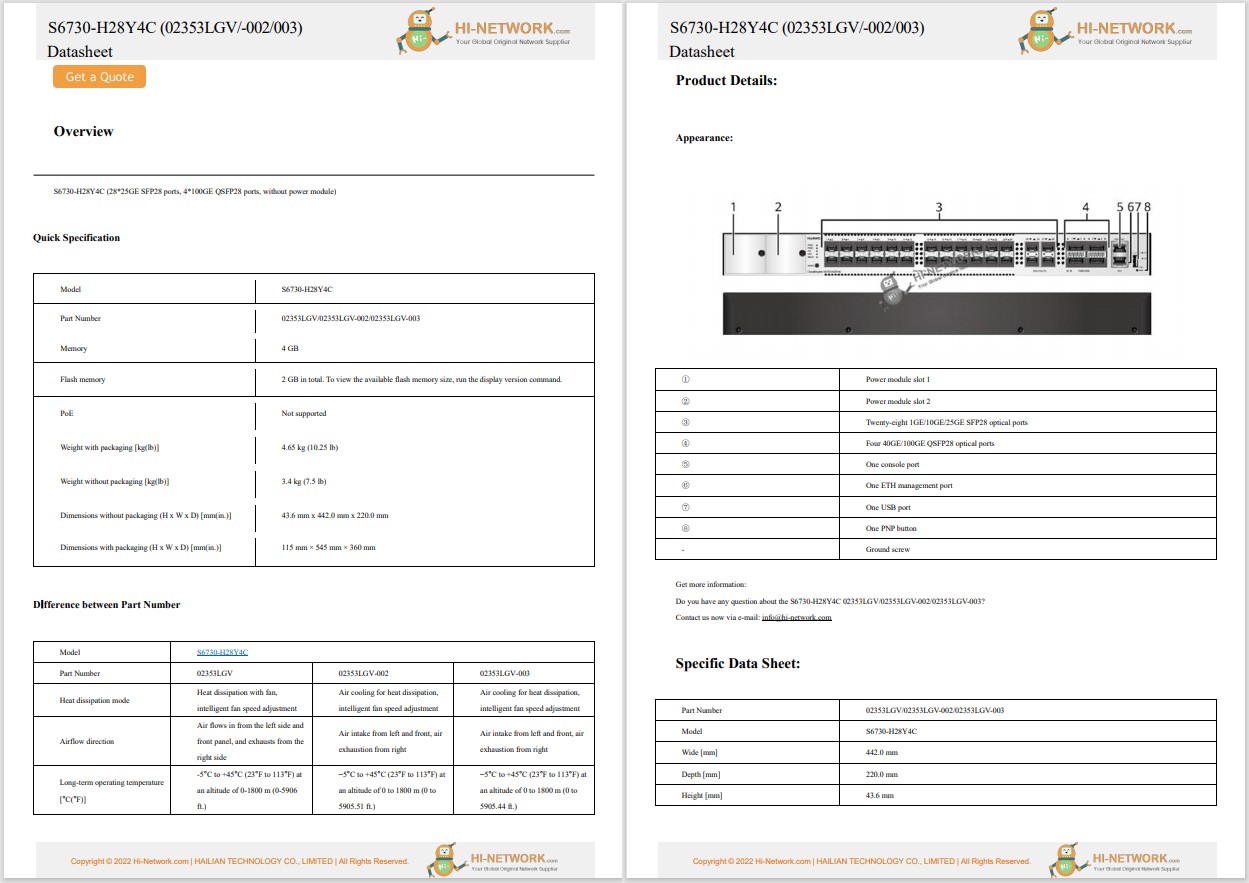


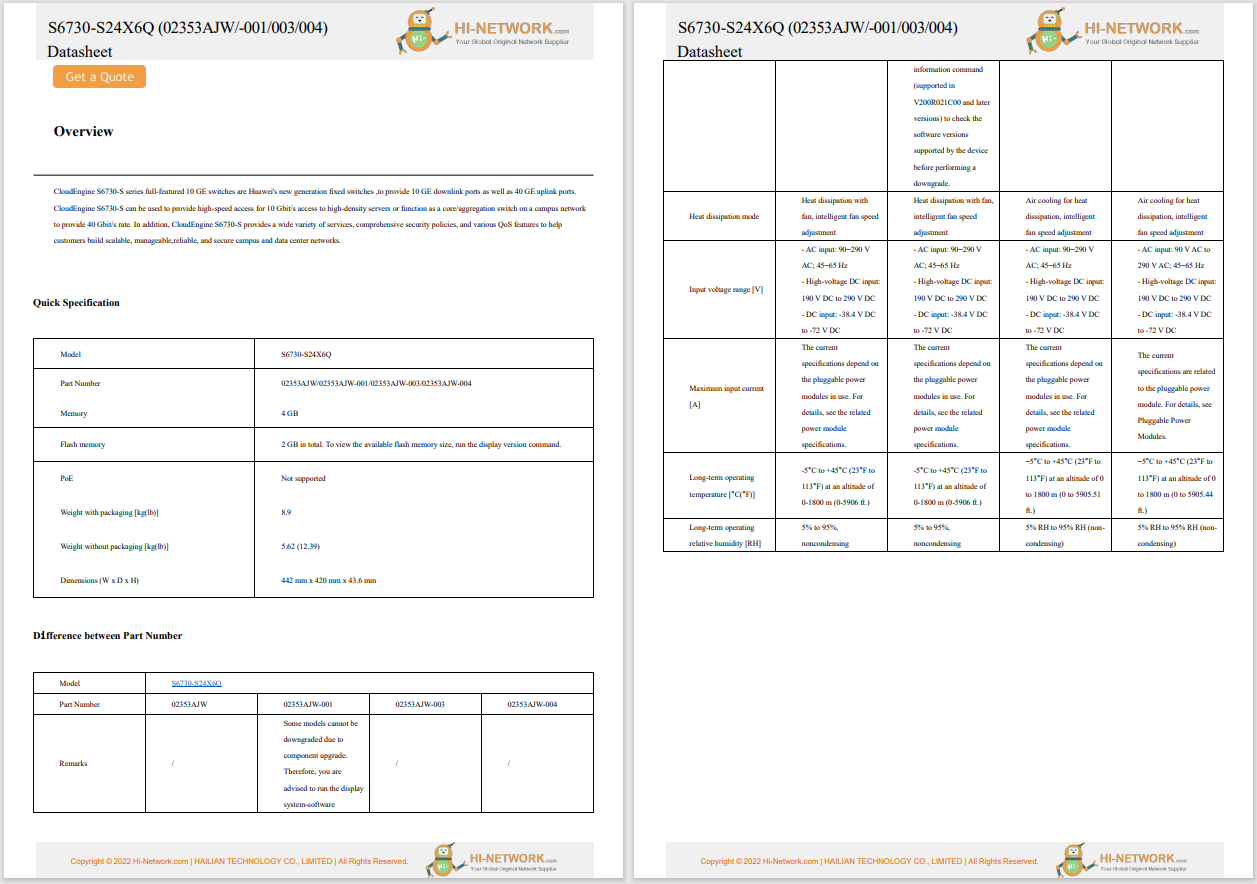
What Is a Wireless Network?
A wireless local-area network (LAN) uses radio waves to connect devices such as laptops and mobile phones to the Internet and to your business network and its applications.
What is the difference between a Wi-Fi or wireless network and a wired network?
A wireless network allows devices to stay connected to the network without being connected by wires. Access points boost Wi-Fi signals, so a device can be far from a router but still stay connected. When you connect to a Wi-Fi hotspot at a café, hotel, airport lounge, or other public place, you are connecting to that business's wireless network.
A wired network uses cables to connect devices, like laptops or desktop computers, to the internet or another network. Compared to a wireless network, a wired network has some drawbacks. The biggest drawback is that your device is connected to a router by a cable. The most common wired networks use cables that are plugged into an Ethernet port on the network router and then into a computer or other device.
In the past, it was believed that wired networks were faster and more secure than wireless networks. However, continuous improvements in wireless network technology, such as the Wi-Fi 6 networking standard, have reduced the speed and security differences between wired and wireless networks.

What are the advantages of having a Wi-Fi wireless network?
Convenience: You can access your network resources from anywhere within the coverage area of your wireless network or from any Wi-Fi hotspot.
Mobility: Unlike a wired connection, you are not restricted to your desk. You and your employees can go online during conference room meetings, for example.
Productivity: Wireless access to the Internet and your company's important applications and resources helps your staff complete their tasks and promotes collaboration.
Easy setup: Setting up a wireless network is quick and cost-effective because you don't have to connect cables.
Expandability: It is easy to expand wireless networks using existing equipment, while a wired network may require additional wiring.
Security: Wireless networks now offer strong security measures to protect your data.
Cost reduction: Wireless networks can be cheaper to operate compared to wired networks because they eliminate or reduce the need for wiring expenses.
To set up your wireless network, you have three options: centralized deployment, converged deployment, and cloud-based deployment. If you need help deciding which one is right for your business, talk to an expert.
1. Centralized Deployment
Centralized deployments are the most common type of wireless network system. They are typically used in places like campuses where buildings and networks are close together. This type of deployment consolidates the wireless network, making upgrades easier and allowing for advanced wireless features. The controllers are located on-premises in a central location.
2. Converged Deployment
Converged deployments are ideal for small campuses or branch offices. They provide consistency in both wired and wireless connections. In this type of deployment, wired and wireless connections are combined into one network device called an access switch. This device serves as both a switch and a wireless controller.
3. Cloud-Based Deployment
Cloud-based deployment uses the cloud to manage network devices that are located on-premises in different locations. This solution requires Cisco Meraki cloud-managed devices, which give you complete visibility of your network through their dashboards.
If you have more questions about networking solutions, you could contact us www.hi-network.com (Email: info@hi-network.com)
 Hot Tags :
network
Hot Tags :
network