



























Hello everyone, many people have recently been asking about how two routers on different network segments can communicate with each other. To solve this problem, we need to configure static routing. Although routers in home networks usually use bridging function, static routing configuration is more common in projects, especially for enabling communication between routers in different network segments. Some of you may have doubts about the specific configuration of static routing. Today, let's take a closer look.
In this article, we will provide three similar examples to explain static routing configurations. This article contains technical content, but it is also very practical. We recommend that you read it carefully.
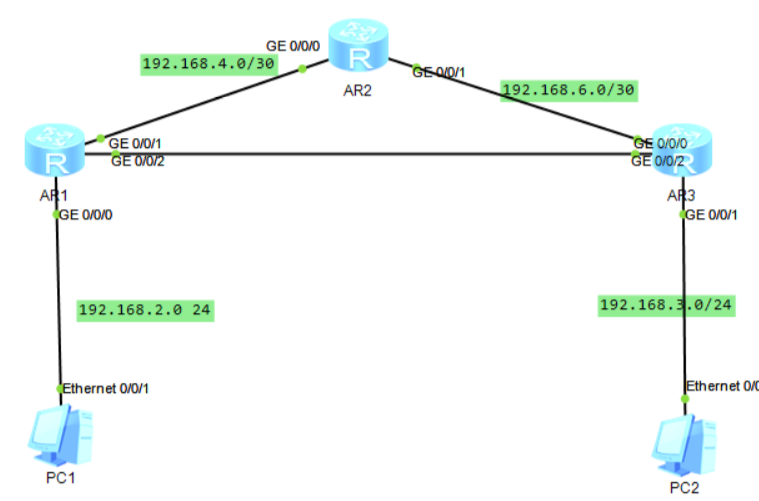
Case 1: What is a static route?
When two routers are connected to different network segments, we need to configure static routing in order to enable communication between the two network segments.
Case 2: How to configure static routing?
Let's say an enterprise accesses the Internet through router R1 and has a local area network (LAN1). For business purposes, they added a router R2 and a new LAN segment (LAN2). To allow PC1 in LAN1 and PC2 in LAN2 to communicate with each other, we can make the following settings:
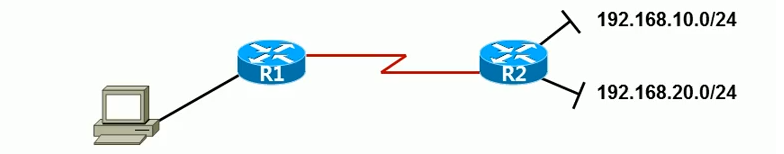
- Set the gateway of PC1 to be the LAN interface of R1.
- Set the gateway of PC2 to be the LAN interface of R2.
- Set the gateway of R2's WAN interface to be the LAN interface of R1.
- Specify a static route on R1, so that data packets with destination IP in the 192.168.1.x network segment are forwarded to R2.
Case 3: Solve the configuration of static routing again
Suppose we have two network segments as follows:
PC A: 192.168.0.165 255.255.255.0
PC B: 192.168.0.148 255.255.255.0
In the above diagram, PC A and PC B belong to different network segments. In this case, B can ping A, but A cannot ping B. The reason is that after PC B's IP passes through the router's network address translation (NAT), the external display becomes 192.168.0.148, and PC A does not know the real existence of PC B.
To enable PC A to ping PC B, we need to inform PC A how to access PC B. We can add a static route on PC A by entering the following command in the command prompt (or terminal):
route -p add destination address mask subnet mask gateway address
The meaning of this command is that if you want to find the "destination address," send the data packet through the "gateway address." The -p flag means the route will have a permanent effect.
So, based on the example above, the command should look like this: route -p add 192.168.19.0 mask 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.148
Here, 192.168.19.0 represents all IP addresses under the 192.168.19 network segment. After adding the route, you can use the route print command to check if the addition was successful. (Note that on Windows 10, you need to run Command Prompt as administrator to add static routes).
Conclusion:
Step outside the limits of your network and discover the best connection! Visit Hi-Network.com today and buy the latest routers, switches, and network equipment to instantly enhance your network experience!
Check More Hi-Network Products:
 Hot Tags :
network
ROUTERS
Hot Tags :
network
ROUTERS