
















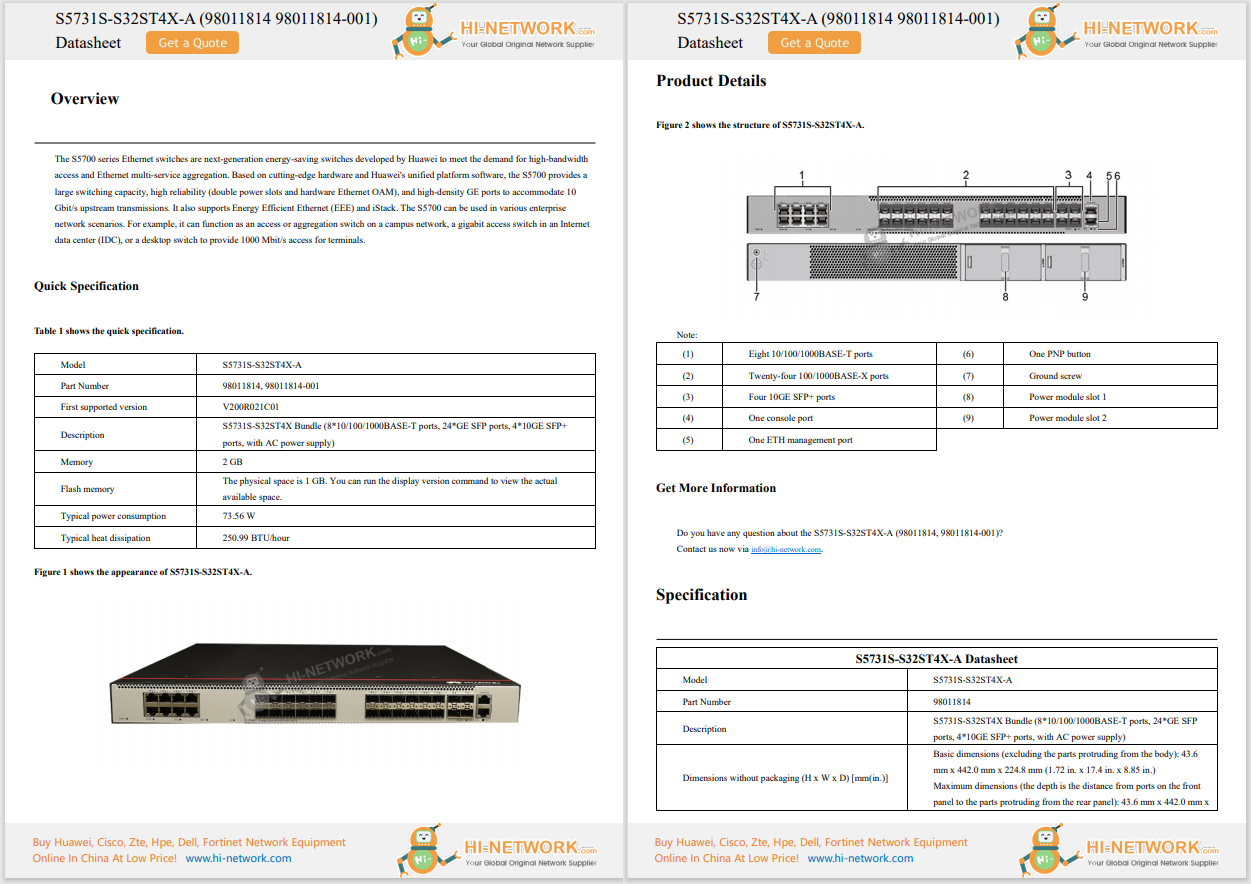












If you have made careful choices regarding routers, it is expected that you are commencing with models that offer convenient setup tools such as a mobile app or web dashboard. As each router possesses unique characteristics, the setup process will vary. The following are fundamental steps that should be universally applicable to all router configurations.

Before you begin
Check your Internet connection
If your Internet connection is not stable, the setup process for the router will be frustrating. The easiest way is to connect a computer to the modem or gateway device provided by your Internet service provider (ISP). If your computer detects an Internet connection, you are ready to proceed with the router setup.
Gather necessary documentation
This step may seem obvious, but it will save you from frustration during the setup process. Look for stickers or slips of paper that contain important setup information, such as the default username and password for the router.
Check for available apps
Many router manufacturers offer mobile apps or web dashboards that can be used for both setup and management. With a smartphone app, you may not need to connect the router to a computer in order to configure it. Check the documentation that came with your router to see if an app is available.
Install and extend antennas
If the router has separate antennas that are not attached to the router box, you will need to install them. Additionally, it is recommended to extend the antennas before starting the setup process.
Router setup steps
Step 1: Determine the placement of the router
The ideal location for a wireless business router is in an open area of the workplace to ensure even coverage. However, finding an open space may not always be easy as the router needs to be connected to a broadband gateway from your ISP, which is usually near an outside wall.
Step 2: Connect to the Internet
Connect the router with a cable or consider a mesh router
To solve the issue of long-distance connectivity when setting up a router, you can use a CAT5e or CAT6 cable to connect the router to the Ethernet port of the ISP gateway. Another option is to run Ethernet cables through the walls of your office to the central location where the router will be placed.
Alternatively, you can install a mesh network with a router. A mesh network allows you to place multiple Wi-Fi transmitters across your home or office, all connected to one network. Unlike extenders, which can be used with any wireless router, mesh networks require a router with this capability built-in.
Regardless of the option you choose, you will need a basic Ethernet cable to connect the router's wide-area network (WAN) or Internet port. The Internet port is usually distinguished by a different color from the other ports.
Check the router's LED lights
The LED lights on your router indicate if you have successfully established an active Internet connection. If you do not see any lights confirming the connection, ensure that you have plugged the cable into the correct port.
Test the connection with a device
Verify that your router has a working connection by connecting a laptop computer to one of the device ports on the back of the router. If everything is functioning properly, you should be able to establish a wired connection, similar to when confirming an active Internet connection.
Step 3: Configure the wireless router gateway
In some cases, ISPs provide customers with gateways that have built-in routers. However, these combined devices are usually not designed for business environments and lack additional ports, security features, and options for network expansion as the business grows.
If you have a gateway with an integrated router, you will need to configure the gateway to disable the router and allow the WAN IP address (the unique Internet protocol address assigned to your account by the ISP) and all network traffic to pass through to your new router.
Failure to complete this step may result in conflicts that prevent devices from functioning properly. You may need to seek assistance from your ISP to complete this configuration.
Step 4: Connect the gateway to the router
First, turn off the gateway. If there is already an Ethernet cable plugged into the local-area network (LAN) port of the gateway, unplug it and connect it to the WAN port of your router. Turn the gateway back on and wait a few minutes for it to boot up. Plug in the router's power supply and turn it on, again waiting a few minutes.
Step 5: Use an app or web dashboard
The easiest way to proceed with the router setup is to use a mobile app if provided by the router manufacturer. If there is no app available or you prefer to use the router's web-based dashboard, connect the router to a computer using an Ethernet cable.
You may find the router's IP address printed on the back of the device itself. If not, you can try typing 192.168.1.1, a commonly used router address, into the browser's search bar.
Step 6: Create a username and password
To configure the router, you will need to log in using the default admin username and password. This information is usually printed on the router or provided in the user manual.
After logging in, enter the required credentials. It is highly recommended to immediately create a new username and password, as the defaults are typically not secure (e.g., "admin" and "password1234"). Change them as soon as possible.
Step 7: Update the router's firmware
Your router may require a firmware update, which is the software that operates it. It is important to update the firmware as soon as possible, as the new version may fix bugs or offer enhanced security protections.
Some routers may automatically download firmware updates, but many do not. You may need to check for updates through the app or browser interface.
Step 8: Create a Wi-Fi password
Most routers come with preassigned Wi-Fi usernames and passwords. You will likely be prompted to change the Wi-Fi username and password during setup. If not, it is recommended to change them promptly.
Step 9: Utilize auto-configuration tools when available
If your router is equipped with auto-install features, take advantage of them to simplify the setup process. For example, you can use auto-configuration to manage IP addresses with the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), which automatically assigns IP addresses to devices. These addresses can always be changed later if needed.
Step 10: Set up security
Many router manufacturers provide security features to protect network and user privacy. You can access the web dashboard and enable additional security functionalities such as firewall, web filtering, and access controls to safeguard against malicious traffic. You can also establish virtual private networks (VPNs) for enhanced privacy.
If you have more questions about Cisco Routers and Cisco Switches. You could contact us www.hi-network.com (Email: info@hi-network.com)
 Hot Tags :
Cisco Routers
ROUTERS
Hot Tags :
Cisco Routers
ROUTERS