














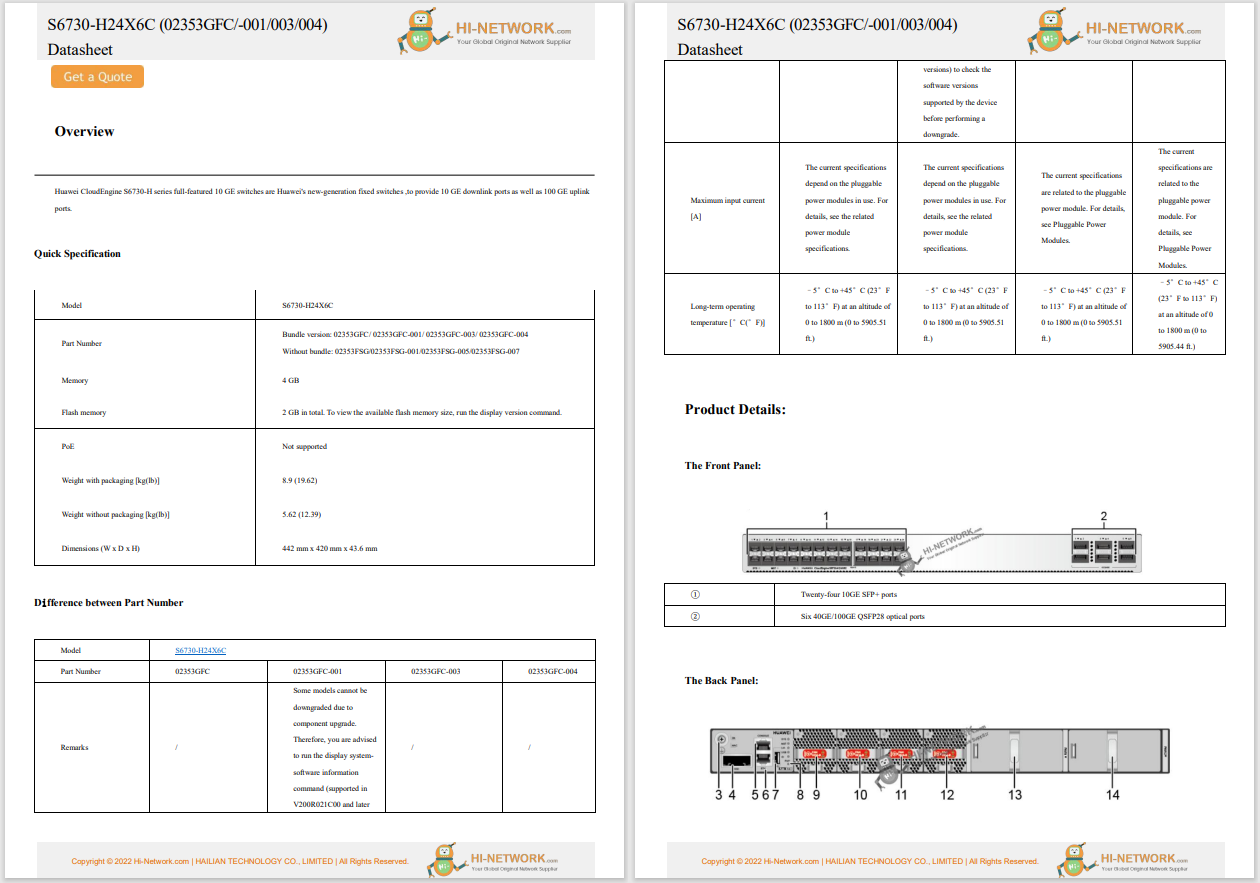

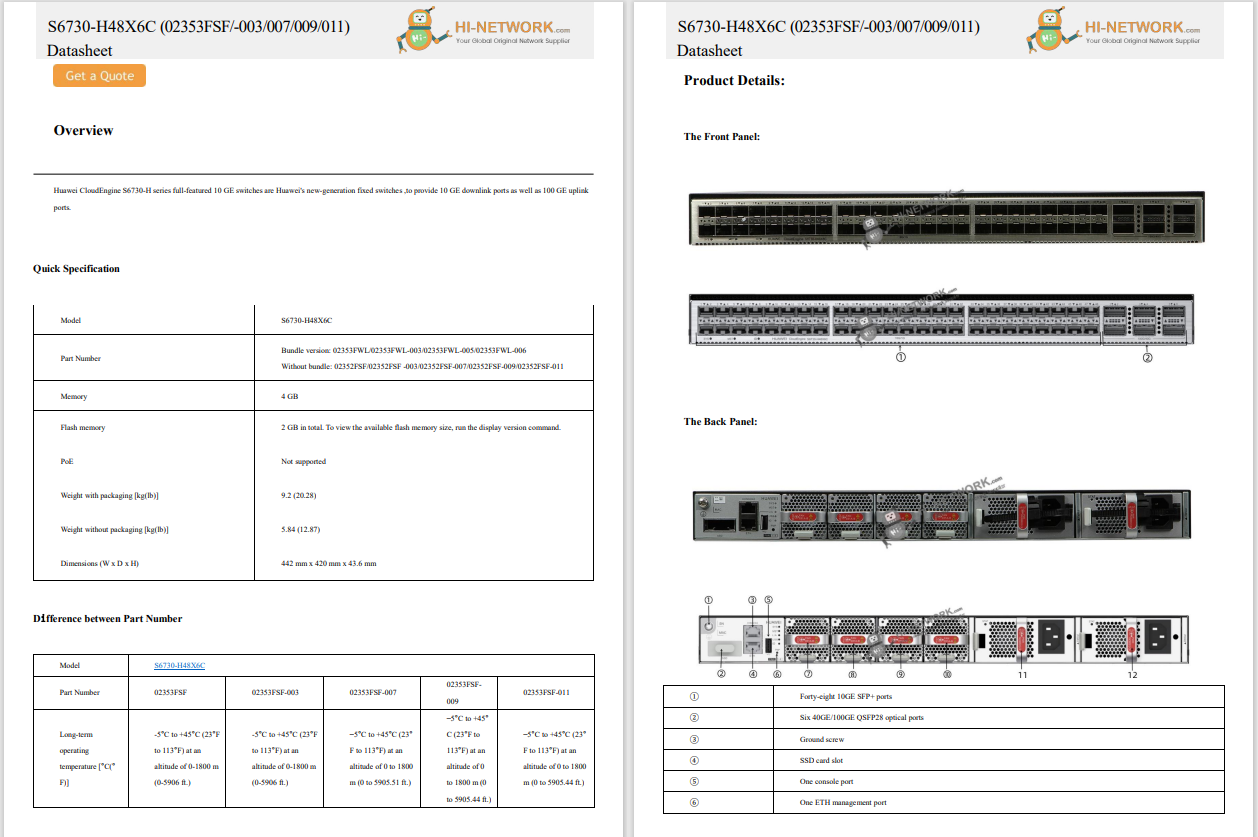











South Africa's Department of Communications and Digital Technologies (DCDT) and Huawei South Africa have partnered to enhance the country's digital economy by expanding its broadband networks, particularly fiber connectivity. The collaboration aims to support small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in building technical capabilities and contribute to broader broadband development efforts.
This initiative follows Huawei's advisory role in the BRICS ICT Development Agenda and Action Plan, where they assist in developing digital economy policies and infrastructure aligned with the National Development Plan 2030.
The partnership seeks to position South Africa as a hub for digital innovation. Despite international concerns, South Africa is strengthening its economic ties with Huawei and China. This stance is not unique to South Africa, as other countries like Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa (BRICS) have also deepened their partnerships with the Chinese company.
Why does it matter?
The partnership between South Africa and Huawei to advance the country's digital economy and broadband infrastructure holds critical significance amid a complex relationship of economic, technological, and geopolitical forces. This dynamic could hold for other nations within the BRICS grouping, particularly given its recent expansion to include six new countries. The profile of some of these countries underscores the reality that fostering their digital economy requires technological advancement and considerable foreign investment, which China can offer.
 Hot Tags :
Capacity development
Critical internet resources
Hot Tags :
Capacity development
Critical internet resources