

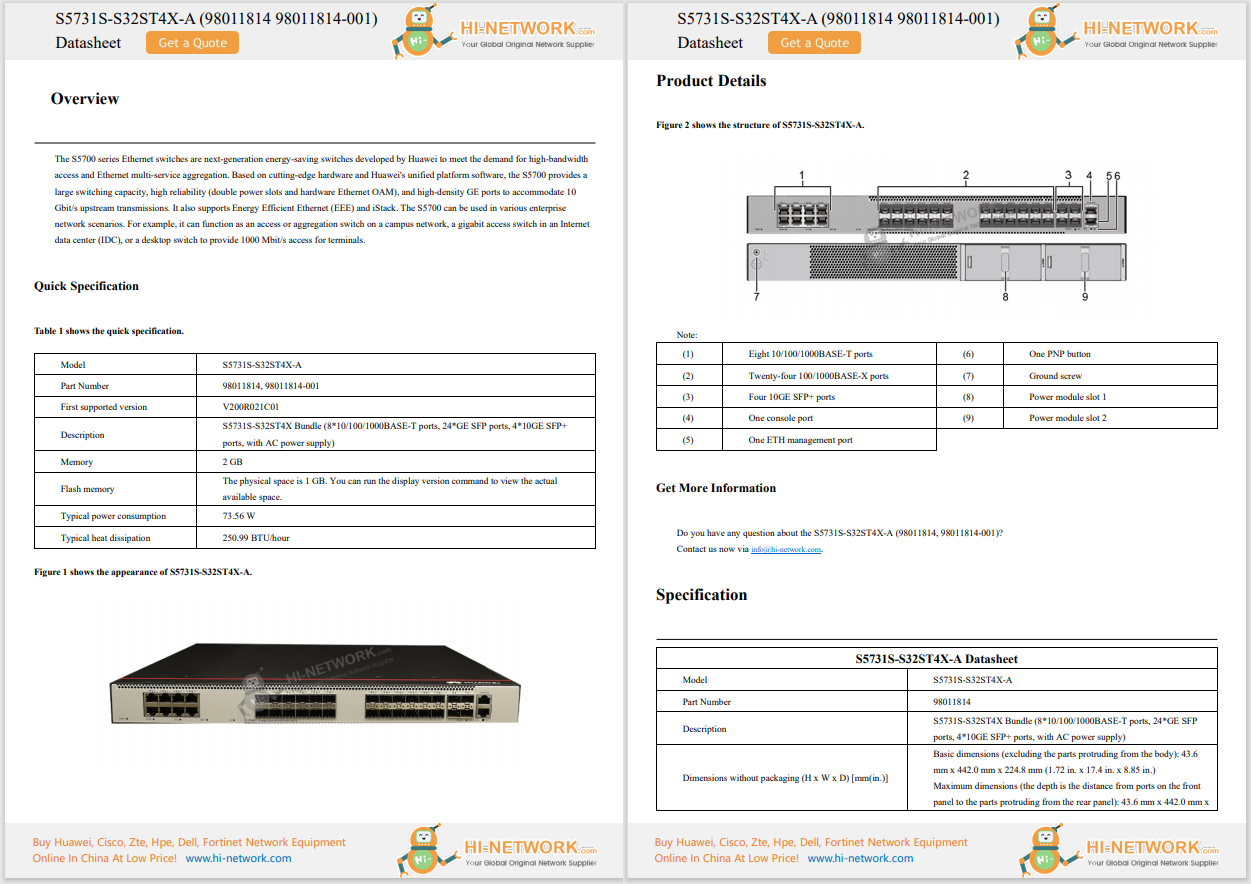











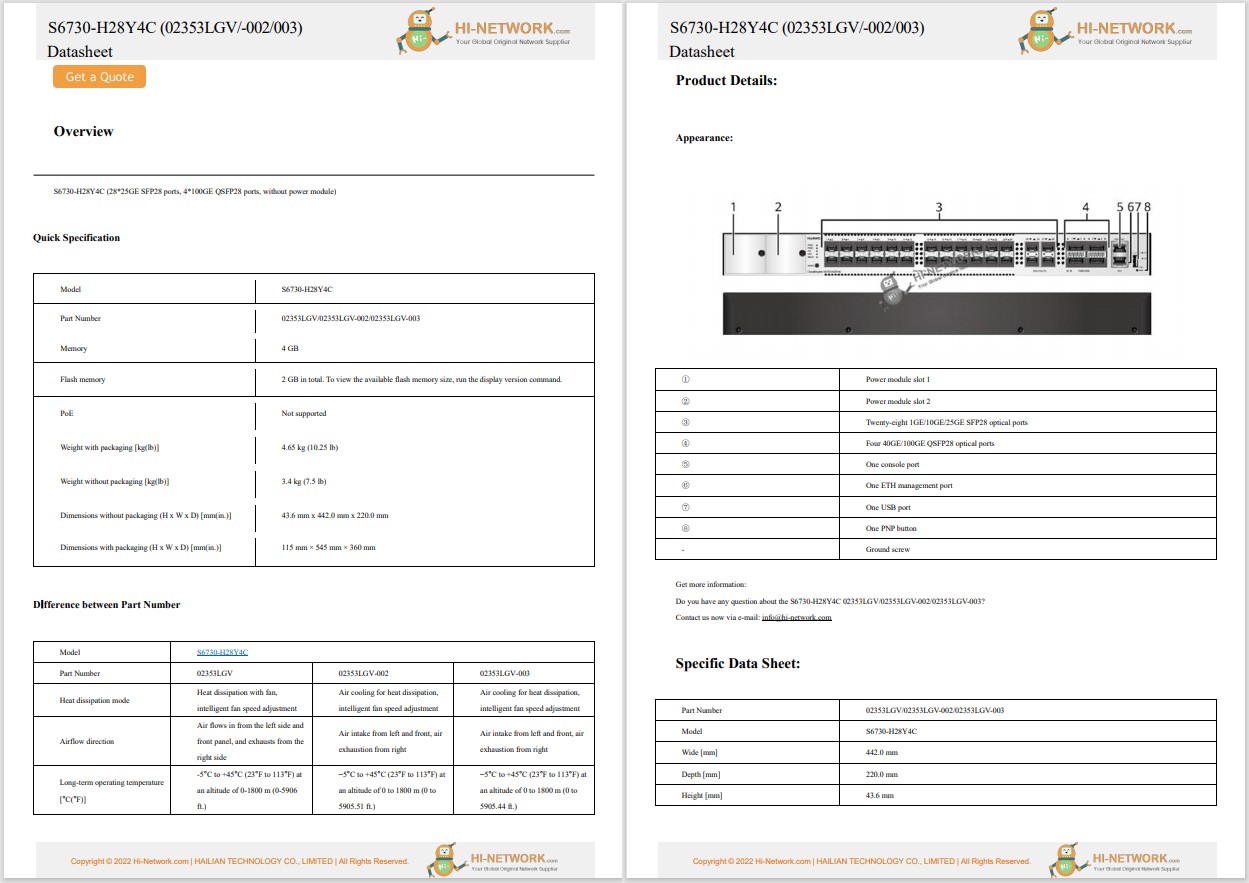


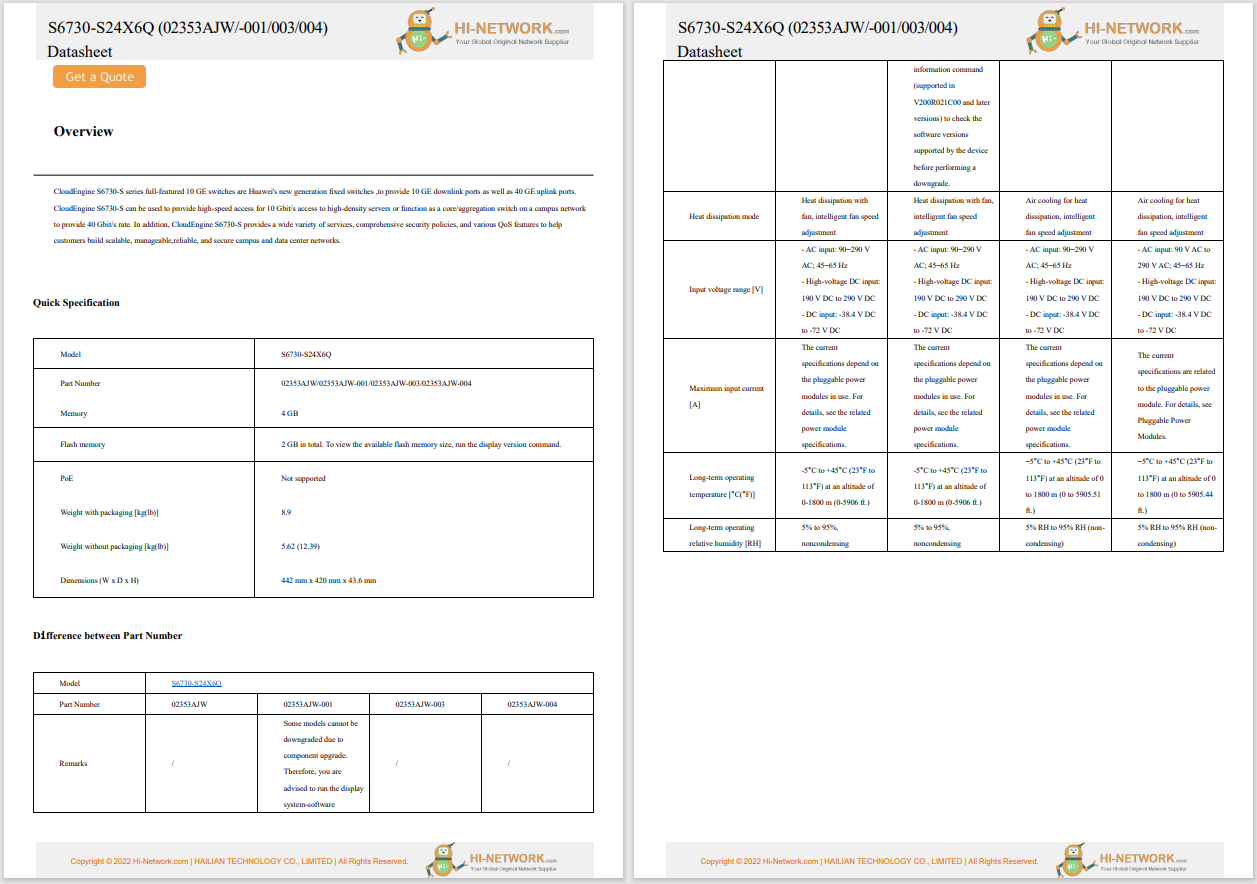










Internet or Net Neutrality means that there are no restrictions of any kind on access to content on the web, no restrictions on downloads or uploads, and no restrictions on communication methods such as email, chat, and IM.
It also means that access to the internet will not be blocked, slowed down, or sped up depending on where that access is based or who owns the access points. In essence, the internet is open to everyone.
When we get on the web, we can access the entire web. That means any website, video, download, or email. We use the web to communicate with others, go to school, do our jobs, and connect with people worldwide. When Net Neutrality governs the web, this access is granted without any restrictions whatsoever.
These are a few reasons Net Neutrality is important:
Strong Net Neutrality rules should be left in place to ensure these things exist and thrive. With Net Neutrality rules now approved for repeal by the U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC), everyone who uses the internet is expected to lose these freedoms.
Internet fast lanes are special deals and channels that would give some companies exceptional treatment as far as broadband access and internet traffic. Many people believe that this would violate the concept of Net Neutrality.
Internet fast lanes could cause issues because instead of internet providers being required to provide the same service for all subscribers regardless of size, company, or influence, they could be able to make deals with certain companies that would give them preferred access. This practice could potentially hamper growth, strengthen illegal monopolies, and cost the consumer.
In addition, the open internet is essential for a continued free exchange of information, a bedrock concept that the World Wide Web was founded upon.
No. There are countries, now including the United States, whose governments want to or have restricted their citizens' access to the web for political reasons. Vimeo has a great video on this topic that explains how limiting access to the internet can impact everyone in the world.
In the U.S., the 2015 FCC rules were intended to give consumers equal access to web content and prevent broadband providers from favoring their own content. With the FCC's vote to remove Net Neutrality on December 14, 2017, those practices will now be allowed as long as they are disclosed.
Yes, as evidenced by the 2017 FCC vote to remove Net Neutrality regulations. Many companies have a vested interest in making sure that access to the web is not freely available. These companies are already in charge of most of the web's infrastructure, and they see potential profit in making the web "pay for play."
Net Neutrality 2021 LegislationIn 2019, a D.C. circuit court ruled that the FCC acted within its rights to roll back Net Neutrality protections. However, the ruling also said that states could put their own protections in place. It remains possible the FCC rollback could be struck down in the future.
At Fight for the Future's Battle for the Net site, you can still contact your representative to tell your position on Net Neutrality. The site prompts you to fill in information to send an email automatically to your area's congressperson. Fill in your name and other requested information, and the site sends the email for you.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/FunctionalFCC-c8f97fe8969e4f5dada59e60a0a300d0.jpg)
When you complete the email form, a message appears asking if you want to share your action via X (formerly Twitter) or Facebook with key decision-makers tagged for you.
If you have your own site, show your support for the rollback, and inform your site's visitors about the issue, too. Battle For The Net is running a Red Alert campaign that offers a widget; avatar images; X, Facebook, and Instagram images; and banner ads that site owners can use to make their own statement about the issue.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Writelawmakers-c9745c060bef4f58b5464c95906d0db7.jpg)
Net Neutrality is the foundation of the freedom that we enjoy on the web. Losing that freedom could result in consequences such as restricted access to websites and diminished download rights, as well as controlled creativity and corporate-governed services. Some people call that scenario the end of the internet.
Net Neutrality in the context of the web is somewhat new. However, the concept of neutral, publicly accessible information and transfer of that information has been around since the days of Alexander Graham Bell. Basic public infrastructures, such as subways, buses, and telephone companies, aren't allowed to discriminate, restrict, or differentiate common access. This is the core concept behind Net Neutrality as well.
For those of us who appreciate the web and want to preserve the freedom that this amazing invention has given us to exchange information, Net Neutrality is a core concept that we must work to maintain.
 Hot Tags :
Internet
Hot Tags :
Internet