














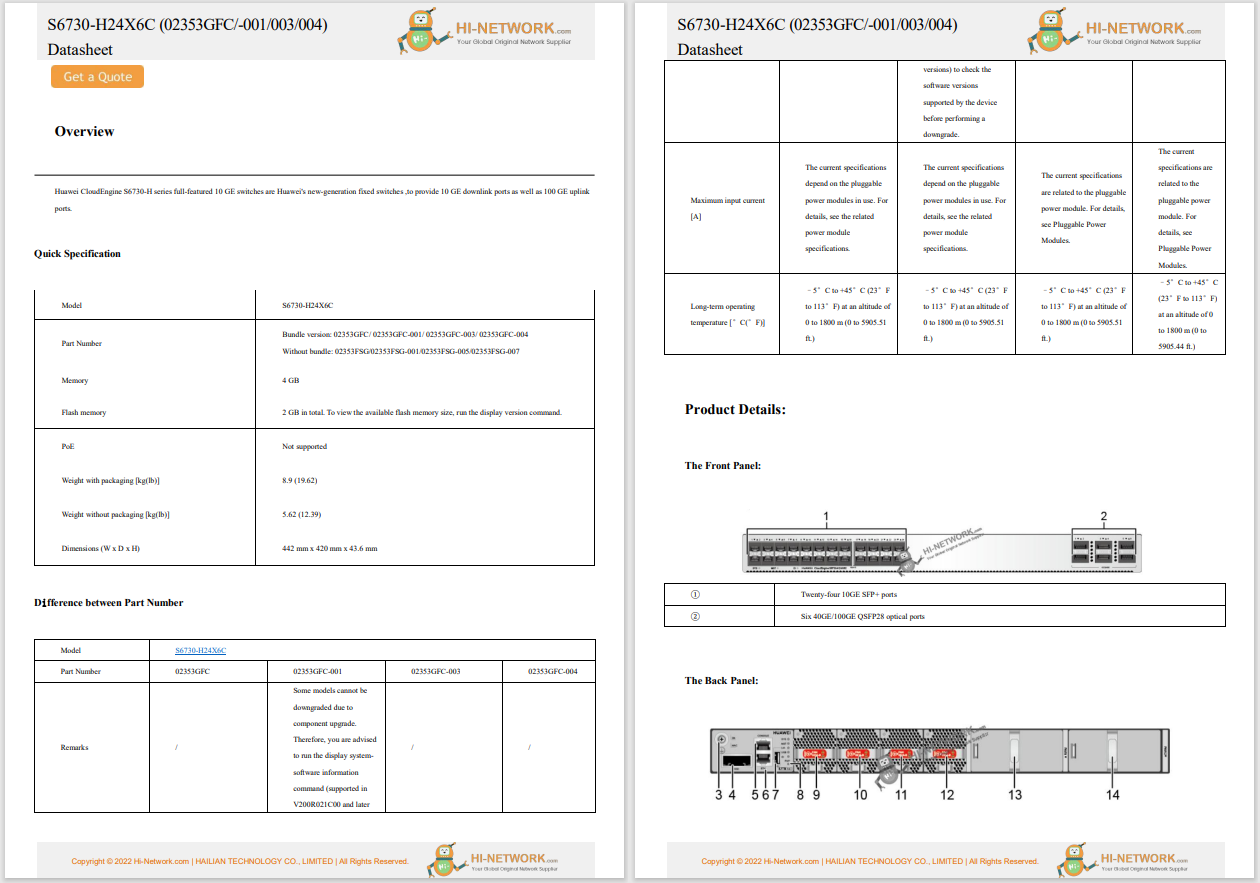











Today, threat actors are increasingly targeting operational technology (OT) infrastructure. According to the Fortinet 2024 State of Operational Technology and Cybersecurity Report, OT organizations struggle to keep up as cyberattacks on OT systems surge by 73%.
But the news isn't all bad. Even though OT professionals report more intrusions and worse outcomes, security is evolving in many organizations. Everything from leadership structure to technologies that protect OT systems are moving forward. Yet even as many organizations improve security, they still face challenges securing converged IT/OT environments.
It's critical for CISOs and other OT leaders to know what is happening in cybersecurity now and what the trends have been over the last few years. This information can help you assess your current cybersecurity maturity by comparing and contrasting your priorities and security strategies with those of your peers.
This is the sixth edition of the Fortinet 2024 State of Operational Technology and Cybersecurity Report. Over the years, several key themes and changes have become evident. The first and most obvious change is that the risk to OT has been validated and elevated to the C-suite.
Six years ago, OT security wasn't a priority. Many organizations excused the lack of security because the factory was air gapped or unconnected from IT systems and associated online threats. However, cybersecurity has become a priority as more organizations have connected their factories and critical infrastructure to the outside world. An ever-increasing number of companies and governments are taking steps to appropriately secure critical infrastructure and vital production systems.
Today, the risks to OT networks and critical infrastructure are finally recognized and prioritized. Once a company realizes and understands that something must be done to mitigate threats, OT security becomes a major priority, and personnel and other resources are assigned to the task.
Over the years, we've seen CISO responsibilities elevated to include OT, which has increased year over year. Interestingly, we also see other members of the C-suite taking on the responsibility for OT, including the CIO, COO, and CTO. Having the CISO and the entire C-suite take on responsibility for OT security and risk mitigation represents a major mindset shift at many organizations.
 Figure 1: Responsibility for OT cybersecurity
Figure 1: Responsibility for OT cybersecurity Another trend is that threat actors are now taking a more targeted approach and focusing on the OT sector. Although the Fortinet survey covers most industrial vertical markets, manufacturing has emerged as a recent target, and we see upticks in brand degradation and loss of business-critical data and intellectual property.
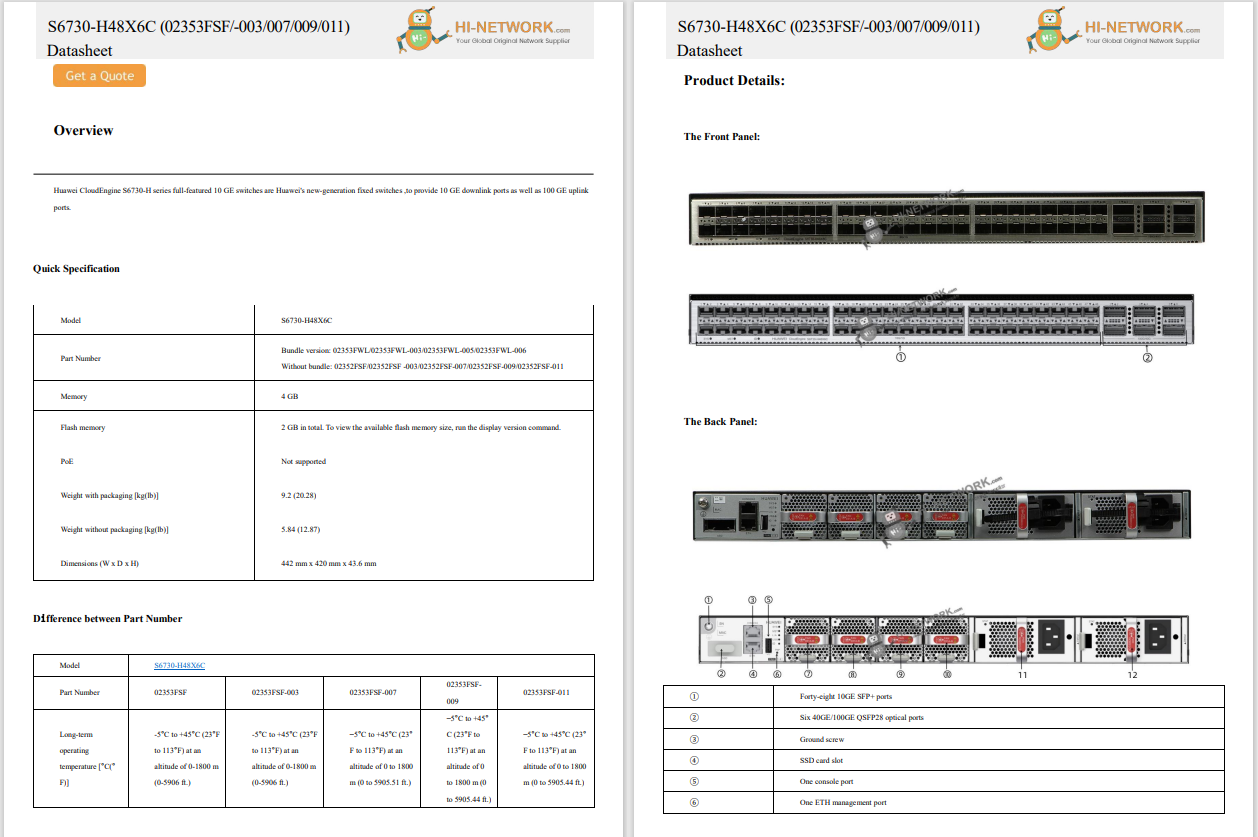
In the survey and through OT threat intelligence, we've observed that bad actors are now monetizing the interruption to production and adding this to their ransom calculus.
 Figure 2: Cybersecurity incidents
Figure 2: Cybersecurity incidents The 2024 survey indicates that two types of attacks on OT environments have become most prevalent. The first is traditional ransomware events that may interrupt or have an operational impact on critical infrastructure or production.
The second is OT-specific malware that is built to infect, control, or manipulate the physical processes in OT environments like valves, switches, or conveyor belts. Although OT-specific malware attacks are less frequent, they are typically led by nation-state actors who have the resources to design malware to attack a specific type of OT network device to disrupt or gain control of the device and potentially impact the system.
 Figure 3: The impact of intrusions
Figure 3: The impact of intrusions OT organizations continue to have some critical blind spots in terms of modernizing their environments. For example, the factory floor is a wide tapestry of unique and often older production equipment that was designed for reliability. Ten or 20 years ago, security was simply not part of the equation, so these devices and the communication protocols or languages they speak are unique to OT.
To add security to these legacy systems, first you need to start with visibility. You need to see and inventory all the systems you need to protect. Next is a next-generation firewall and switches to segment the OT networks. As the organization's security becomes more mature, you can then bring in aspects of the zero-trust network security model. Finally, you can add advanced security operations (SecOps) for OT.
Security maturity follows a definite progression, and we see in the report that most organizations are still at the beginning of their journey. Visibility and segmentation have increased, and we're also seeing an uptick in SecOps. The report shows that there's a wide spectrum of modernization, ranging from basic controls to the most advanced SecOps.
 Figure 4: OT maturity
Figure 4: OT maturity Organizations can take a few practical steps right away to secure OT. As you work to establish proper visibility, separating the OT networks with additional firewalls and switches can help protect vital OT devices and production lines. This network segmentation can prevent bad actors from roaming throughout the OT network.
Because OT devices tend to be old, security patching is another huge challenge for many organizations. The patches may not exist, or there simply isn't time to patch every device. But while you wait for patches, you can still implement compensating controls to reduce the risk to unpatched devices. These controls include microsegmentation, virtual patching, deception, and OT application layer policies to help protect vulnerable devices.
Planning is also key. Look toward the future when you have OT SecOps and consider creating a strategy for a joint IT/OT security operations center. To set up this type of center, you must employ OT-specific SecOps tools to identify and read these unique devices and network communications. Given that most organizations don't have enough skilled cyber workers, you also should look towards OT security vendor consolidation while continuing to respect operational priorities.
Also, evaluate your OT threat intelligence. Although having OT security solutions is important, you also need AI-driven and near-real-time threat intelligence to keep up with today's rapidly shifting security landscape. As you work to aggregate and centralize these varied solutions to optimize resources and time to respond, consider taking a platform approach.
A cybersecurity platform like the Fortinet OT Security platform can help facilitate OT vendor consolidation, another serious challenge for many CISOs. An extension of the Fortinet Security Fabric, the OT Security platform is broad, integrated, and automated and includes secure networking, zero trust, network operations, and security operations solutions. It includes OT-specific solutions and services to help ensure effective performance, along with AI-powered OT threat intelligence to protect against the latest threats.
Get all the details about the state of OT security in theFortinet 2024 State of Operational Technology and Cybersecurity Report. And for more insights, be sure to attendour August 27 webinar, featuring a panel of experts who will discuss the report findings.
 Hot Tags :
Business and Technology
Operational Technology (OT)
operational technology
Hot Tags :
Business and Technology
Operational Technology (OT)
operational technology