












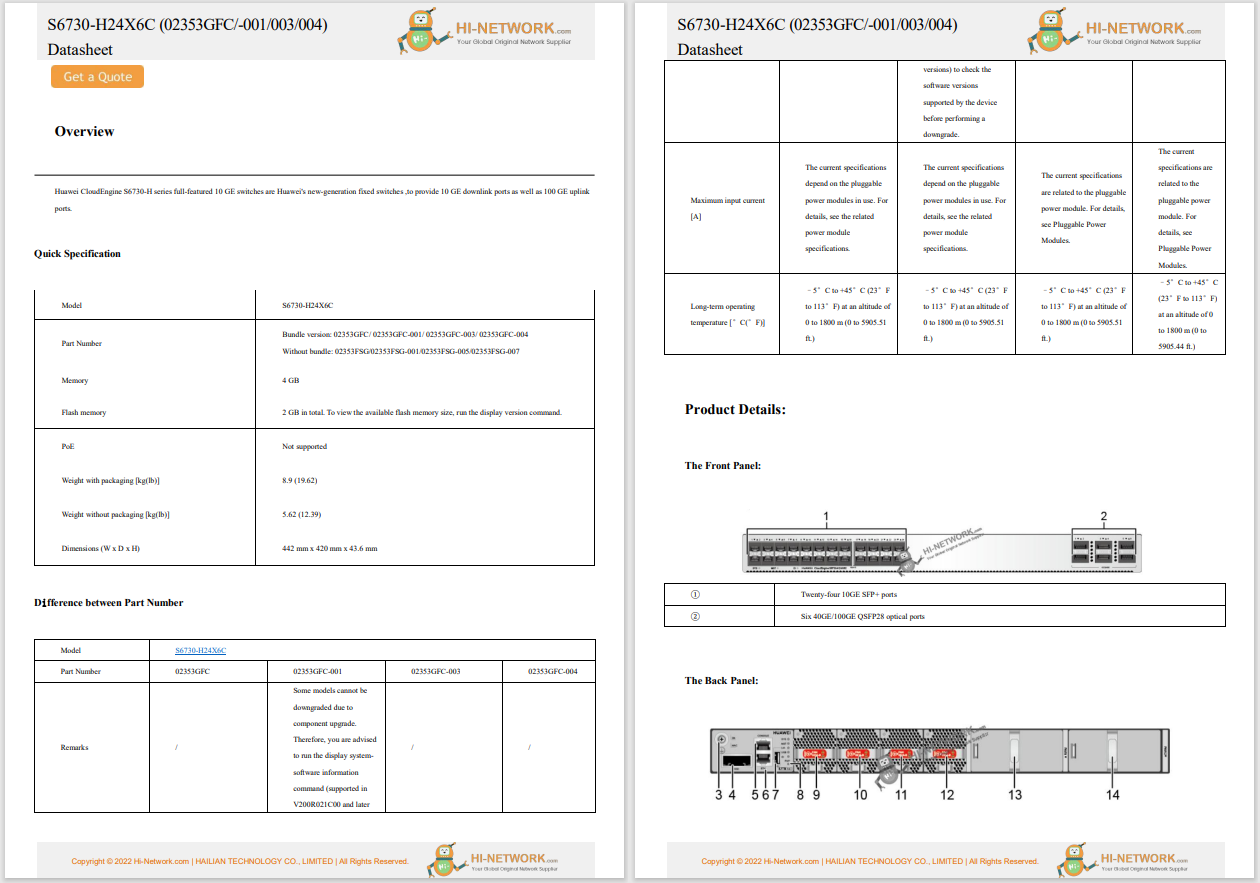

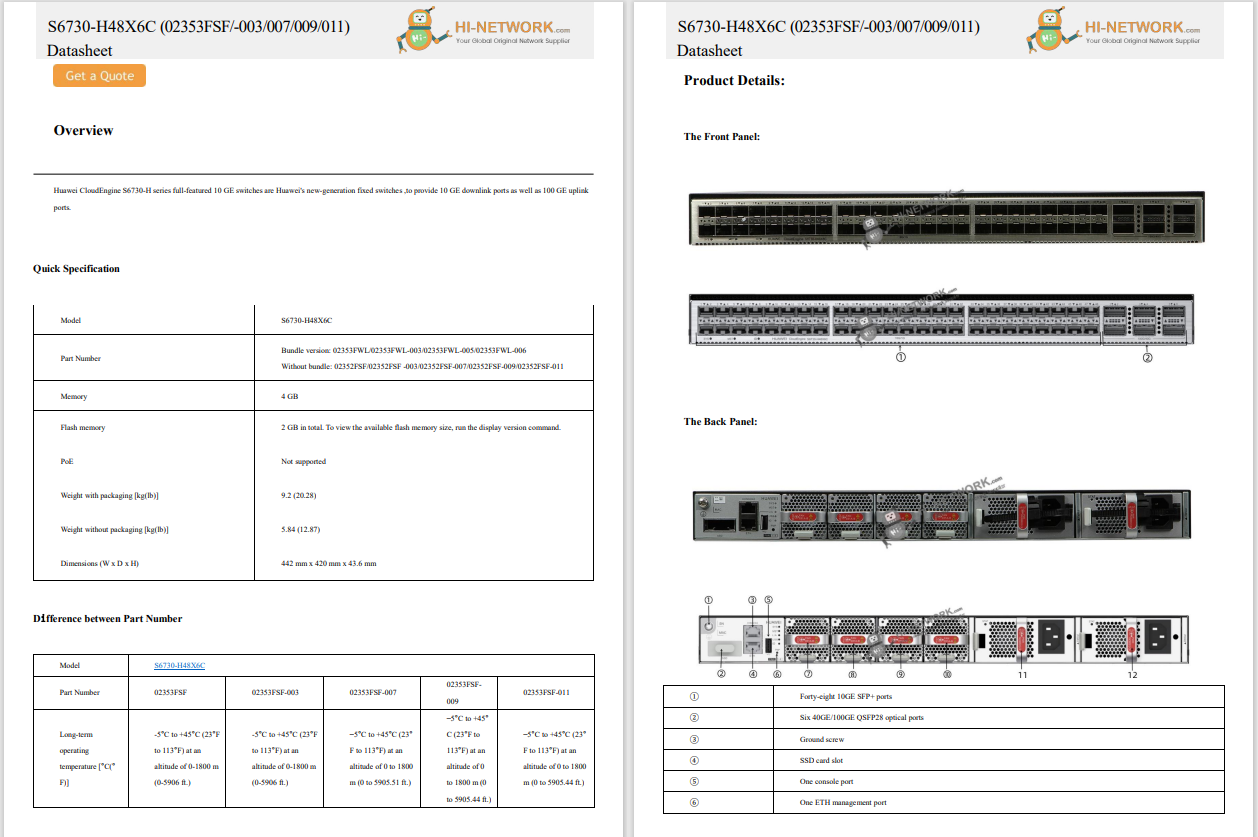












Joining Process of an Cisco Access Point
LAP needs to join to the WLC
(Every device on a network needs to have an ip address, and a LAP is no exception)
1. AP needs ip address in the said order
(1. it has on its own already 2.static 3.dhcp )
(After getting ip address, to join to the WLC, the LAP needs to know what all are those WLCs to which it can join)
2. AP needs to discover WLC via either of the two mechanisms in the said order
[ 1.lyr2 2.lyr3 (makes list of discovered WLCs via 5 mandatory steps) ] <-- Hunting for the WLC
(Once the LAP has list of all those WLCs to which it can join, the LAP can decide the WLC , it will like to join.
The logic for that decision can either be customized by the user or can be left to the default-logic).
The order of execution of logic is preferred with the customized logic first, else with default-logic.
3. AP needs to select one of the discovered WLCs.
4. AP needs to join the selected WLC.
1= A LAP issues a DHCP discovery request to get an IP address, unless it has previously had a static IP address configured.2= The LAP sends LWAPP discovery request messages to the WLCs.
Any WLC that receives the LWAPP discovery request responds with an LWAPP discovery response message.
These WLCs can be either in local or remote subnets. This way, there can be many WLCs which may respond a single LWAPP Discovery Request. A list of all those WLCs is prepared.
3= From the [various(if many WLCs)] LWAPP discovery responses, the LAP receives, the LAP selects a WLC to join.4= The LAP then sends an LWAPP join request to the WLC and expects an LWAPP join response.
#Explanation of 2
(Also known as Layer 2 LWAPP Mode )
If [ (L2 Mode supported on the LAP) && (WLC Discovery Succeeds)]
{LAP broadcasts an LWAPP Discovery Request in a Layer 2 LWAPP frame. Any WLC that is connected to the network and that is configured for Layer 2 LWAPP mode responds with a Layer 2 discovery response, EXIT}
Else
{Discovery Algorithm in Layer 3 ( 'debug lwapp event enable' and 'debug lwapp packet enable')}
(Also known as Layer 3 LWAPP Mode )
If (No Response to Discovery Request)
{ AP Reboots. Go to 1}
Else
{The AP explores via five ways to get the ip address of the WLCs to make the WLC-Candidate-List}
Note: To find the methods being used to discover the ip address of the WLC by the AP, we can run 'debug lwapp packet enable ' and search for the following output in the debug:
IE Length : 1
Decode routine not available, Printing Hex Dump
00000000: ?
This debug can help to find if at the AP is able to find any WLC.
? -> Method used
01 - static ( 'capwap ap controller ip address' || 'previous memory' )03 - dhcp server ( DHCP Option-43 )00 - broadcast (works well when AP and WLC are in same subnet)02 - OTAP ( disabled, by default)(not preferred)(can work only when AP has joined to the WLC )04 - dns ( 'cisco-capwap-controller' via DHCP option 15)if (? == 01){If the LAP was registered to a WLC in a previous deployment, the LAP maintains the list of WLC IP addresses locally in NVRAM. The stored WLC IP addresses include all of the WLCs that are in previously joined WLC "mobility groups". Hence, we may like to make the AP forget all of the previously learnt ip addresses of the WLC by using the , 'clear ap-config ap_name command', in order to reset the LAP to the factory defaults.
1. Discovery Request is Unicast by the LAP.
Can be received by Local WLCs, directly.
Can be received by Remote WLCs, indirectly (via IPHelper cmd).
{Received LWAPP DISCOVERY REQUEST from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 to ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff on port '1'}2. Discovery Response is Unicast to the requesting AP, by the WLC.
{Successful transmission of LWAPP Discovery-Response to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 on Port 1}}if (? == 03){When an LAP gets an IP address from the DHCP server, the LAP looks for WLC IP addresses in the option 43 field of the DHCP offer. This method is used if the WLC is in remote subnet as that of the AP and we dont want to put the ip address of the WLC in the NVRAM of the AP. Obviously, InterVLAN-Routing must be enabled between the WLC's subnet and that of the AP. Can use any DHCP server that supports option 43.
1. Discovery Request is Unicast by the LAP.
Can be recieved by Local WLCs, directly.
Can be received by Remote WLCs, indirectly (via IPHelper cmd).
{Received LWAPP DISCOVERY REQUEST from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 to ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff on port '1'}2. Discovery Response is Unicast to the requesting AP, by the WLC.
{Successful transmission of LWAPP Discovery-Response to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 on Port 1}}if (? == 00){The LAP broadcasts a Layer 3 LWAPP discovery message on to its local subnet. Any WLC, if any, is also on the same subnet, receives the LWAPP discovery request from the LAP and responds with a Layer 3 LWAPP discovery response.
1. Discovery Request is Broadcast by the LAP.
Can be received by Local WLCs, directly.
{Received LWAPP DISCOVERY REQUEST from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 to ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff on port '1'}2. Discovery Response is Unicast to the requesting AP, by the WLC.
{Successful transmission of LWAPP Discovery-Response to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 on Port 1}}if (? == 02){Already Registered LAPs advertise the WLC's IP address to the yet-to-be-registered LAPs (to assist them to find the WLC) with the use of neighbor messages that are sent over the air. The yet-to-be-registered LAPs
hear these messages and add these discovered WLC's ip address to their WLC-Candidate-List.
1. Discovery Request is Unicast by the LAP.
Can be received by Local WLCs, directly.
Can be received by Remote WLCs, indirectly (via IPHelper cmd).
{Received LWAPP DISCOVERY REQUEST from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 to ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff on port '1'}2. Discovery Response is Unicast to the requesting AP, by the WLC.
{Successful transmission of LWAPP Discovery-Response to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 on Port 1}}if (? == 04){Within the DHCP-OFFER, the DHCP option 15 of the DHCP server refers to the domain name that is provided by the DHCP server (in addition to the ip address of the DNS server) to the the 'AP', so that the AP can use that DomainName for DNS resolution by a DNS server reachable to 'it'.
Hence, once the LAP gets the DNS server's IP address, LAP sends out a DNS query, to the DNS Server, for the DNS-Resolution of the acquired DNS name cisco-capwap-controller. Thus, the DNS server must be pre-configured to return the WLC's IP address(es) for this query.
1. Discovery Request is Unicast by the LAP.
Can be received by Local WLCs, directly.
Can be received by Remote WLCs, indirectly (via IPHelper cmd).
{Received LWAPP DISCOVERY REQUEST from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 to ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff on port '1'}2. Discovery Response is Unicast to the requesting AP, by the WLC.
{Successful transmission of LWAPP Discovery-Response to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 on Port 1}
Debug:
On the AP- > debug dhcp detail
}
Now, gets completely filled the WLC Candidate List , filled by the return values from the sysName field of the Discovery Responses.
Note:
[A] Even though, Management and AP-Manager interface can be put in different subnets, should avoid it.
[B] It is worthwhile to revisit the Point#1 . This is important to know, as many times, an AP doesn't join the intended WLC because of its old memories in its NVRAM.
if (
1.any how the LAP joins the Incorrect WLC, and
2.the Incorrect WLC happens to be part of the another mobility group.
3.the other mobility group doesn't know of the Correct WLC.
)
{ Problem }.
1.Use DHCP option 43 || 15 during initial deployment only.
2.Make DHCP option 43 || 15 visible only to their interested APs.
(Say, some APs are in building A and should join only to the WLC for building A)
(Say, some APs are in building B and should join only to the WLC for building B)
So, we can make
(a) separate DHCP scopes for APs in building A and for APs in building B.
(b) give ip address of different WLCs to the DHCP Option-43 of each scope.
3.Use SSC/MIC of specific APs only to be authorized by specific WLCs.
All APs manufactured after June 2006 have a MIC.
4. Configure ip address of Intended WLCs in the NVRAM of the APs
(this step may make sense for some, but not for others, depending on the situation)
For troubleshooting or for unstable networks, one may prefer to use static ip address
For stable networks, one may prefer to use dynamic ip address
If ( High Availability Tab Configured && Configured WLC IPs found in WLC Candidate List)
{
From the LAP, WLCs are selected from within the WLC Candidate List in the said order in the HA tab of the LAP.
If (Join succeeds) {EXIT}
Else {break;}
}
If (Any WLC found tagged as Master WLC)
{WLC is selected which is tagged as Master and is tried}
if (success) {EXIT} else {break;}
if (! More than 1 WLCs found with same largest capacity for APs)
{ WLC with largest excess capacity is selected; EXIT}
The first WLC is selected which responded first, to the discovery request with a discovery response; Exit
---- So far, a WLC has been finally selected so that Join Request can be sent to him-------
If (the selected WLC has multiple AP-managers on multiple interfaces)
{The AP-manager interface with the least number of APs is selected; EXIT}If ( AP has successfully joined the Selected WLC){ If ( Image on the LAP is not the same as that on the WLC) { if (difference between the image version of the WLC and that of the AP is much) { At times, the AP doesn't join to the WLC; EXIT; (need to upgrade the LAP) }The AP downloads the image from the controller and reboots to load the new image and starts the process all over again from first step. After again joining to the WLC, and ensuring that it has same image as that of the WLC, the AP downloads the configuration from the WLC and goes into the REG state. EXIT.
}
}
Else {Troubleshoot}
To check from the Controller's perspective,telnet/console to the controller, and issue the following debug statements:
debug disable-alldebug mac addr 00:22:bd:19:6c:cedebug capwap events enabledebug capwap errors enabledebug pm pki enable
To check from the AP's perspective,telnet/console to the LAP, and issue the following debug statements:
undebug all // Disables debugs on the AP.debug lwapp client event // Shows LWAPP events for the AP.debug dhcp detail // Shows DHCP option 43 information.debug ip udp // Shows the join/discovery packets to the [(controller)for join requests || (DHCP and DNS)for dhcp/dns queries]
.. reboot LAP, and collect the output got, either on the controller, or the AP (as the case may be), in a file.
{}
the AP checks to make sure it has the same image as that of the controller. If not,
Note:
(1)If ( all the steps mentioned, as above , fail) { The AP keeps on rebooting till powered-ON}
Else {After the LAP selects a WLC, the LAP sends an LWAPP join request to the WLC}
(2)Once a WLC is selected, following two events occur, in the said order:
Event 1: 'LAP' sends Join Request to the WLC to:
1. Join to the WLC 2. To authenticate 'itself' to the WLC
Event 2: 'WLC' sends Join Response to the LAP to:
1. Inform LAP that it has been allowed 2. To authenticate 'itself' to the LAP
(3)The logical LWAPP/CAPWAP tunnel that is created between the WLC and the LAP (that is joined to the WLC), may span across 1 or >1 networks. Each network may run with different media types. Each media type may use different MTU size. Hence, to initiate, and sustain the LWAPPP/CAPWAP tunnel, repetitive fragmentation and de-fragmentation (re-assembly) of LWAPP/CAPWAP frames may be required. The WLC and AP operate under the 1500 byte MTU assumption. It can be configured on the WLC. At the AP or WLC, if the MTU is bigger than 1500 bytes, it fragments the packet and sends the packet across. So, we may need to ensure that MTU size of a network may not affect the Join Process.
(4)if DHCP option-43 or 15 (with a DNS server) is to be used, must ensure that the DHCP is not in the same subnet as that of any of the Dynamic Interfaces configured in the WLC.
So far, we have discussed the order in which an AP searches for the WLCs to which it can join to.
Lets discuss,
If (WLC and AP are in same subnet) {Easiest Method as AP's broadcast received by WLC}
Else
if (DNS available for the AP's site) {Use DNS string option;exit}
elseif (DHCP available for the AP's site) {Use DHCP Option 43 ;exit}
else {capwap ap ip address }
!--- LWAPP discovery request sent to the WLC by the LAP.2
00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Received LWAPP DISCOVERY REQUEST from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 to 00:0b:85:33:52:80 on port '2'
!--The WLC has received a Discovery Request on its Port#2 from an AP with mac-address 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0
!--- WLC responds to the discovery request from the LAP.
00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Successful transmission of LWAPP Discovery-Response to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 on Port 2
!--- LAP sends a join request to the WLC.
00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Received LWAPP JOIN REQUEST from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 to 00:0b:85:33:52:81 on port '2'
!--- WLC responds with a join reply to the LAP.
00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Successfully transmission of LWAPP Join-Reply to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0
!-- LAP registers with the WLC.
00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Register LWAPP event for AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 slot 0
!--- LAP requests for the configuration information from the WLC.
00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Received LWAPP CONFIGURE REQUEST from AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 to 00:0b:85:33:52:81
!--- WLC responds by providing all the necessary configuration information to the LAP.
00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Successfully transmission of LWAPP Config-Message to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0
!--- WLC responds to LAP indicating that SSIDs have been configured and hence AP can start servicing clients
00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Successfully transmission of LWAPP Change-State-Event Response to AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0
!--- WLC gets acknowledgement from the AP indicaing that LAP is up and ready to service wireless clients.
00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 Received LWAPP Up event for AP 00:0b:85:5b:fb:d0 slot 0!
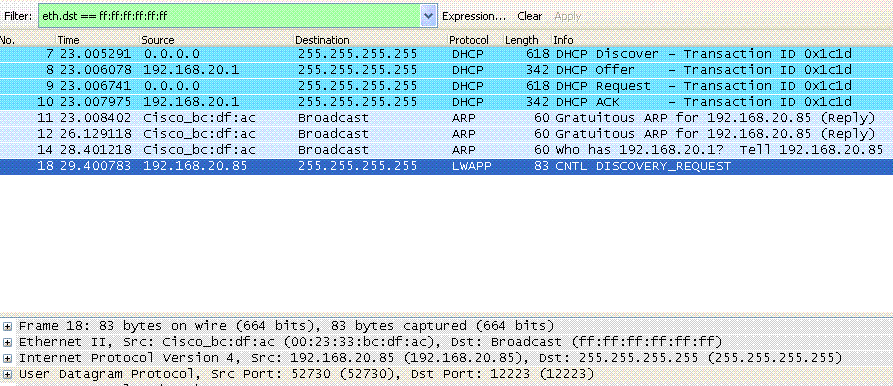
IF (DHCP Option-43 is "A"+"B"+"C" , that is, "ABC"){A is f1.B is HexEquivalent ( countOfNumberOfWLC'sManagementIPAddresses * 4 )C is HexEquivalent ( theIPAddressesOfWLCsInSequentailOrder )Ex: Say, there are two WLCs with management interface IP addresses: 192.168.10.5 and 192.168.10.20.So,A becomes f1B becomes 08To compute C:(1)we know that we want the AP to get the First ManagmentIPAddress of a WLC , ie 192.168.10.5 the SecondManagmentIPAddress of a WLC , ie 192.168.10.20(2) the HexEquivalent of "192.168.10.5" is "c0a80a05"the HexEquivalent of "192.168.10.20" is "c0a80a14""c0a80a05" + "c0a80a14" -> "c0a80a05c0a80a14}THEN{ So, the syntax for configuring the DHCP option-43, within the DHCP server of the Cisco IOS , to return the management ip addresses of two WLCs , when the AP boots up, will be: ip dhcp pool <PoolName> network <ip network> <netmask> default-router <default-router IP address> option 43 hex f108c0a80a05c0a80a14}AP ---- SWITCH --- WLC
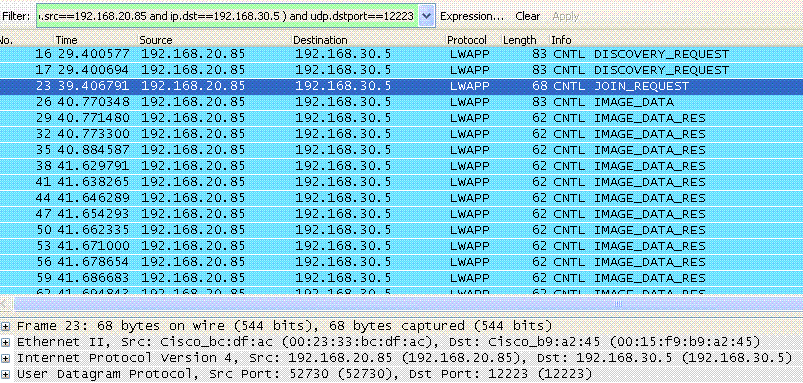
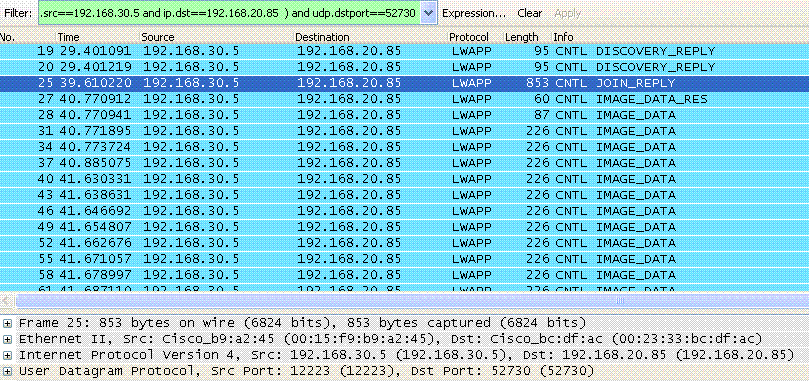
ip 192.168.20.85 192.168.30.5
mac 00:23:33:bc:df:ac 00:23:33:bc:df:ac
udp 52730 12223
12222
1.(a) AP snd ucast discovery request
(b) WLC rcv ucast discovery request
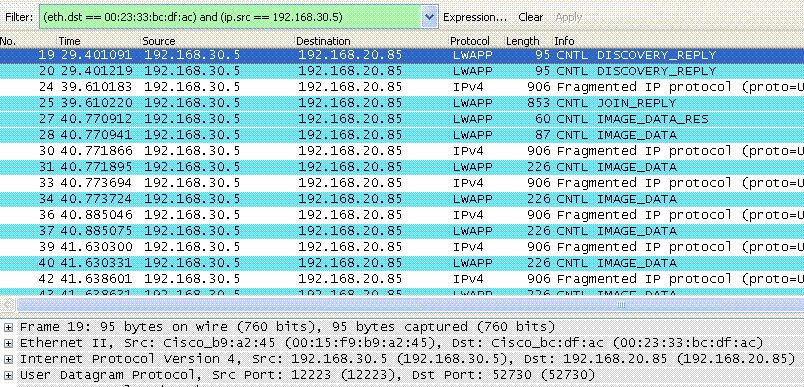
2.(a) WLC snd ucast discovery reply
(b) AP rcv ucast discovery reply
3.(a) AP snd ucast join request
(b) WLC rcv ucast join request
4.(a) WLC snd ucast join reply
(b) AP rcv ucast join reply
Filter:ip.addr==192.168.20.85 && ip.addr==192.168.30.5 can be used to see the communication between AP and WLC.
(the snapshots of the packet captures are in the files, 1a.gif, 2a.gif, 3a.gif, 4a.gif for the steps outlined in steps, 1a, 2a, 3a and 4a, respectively)
Issues while joining
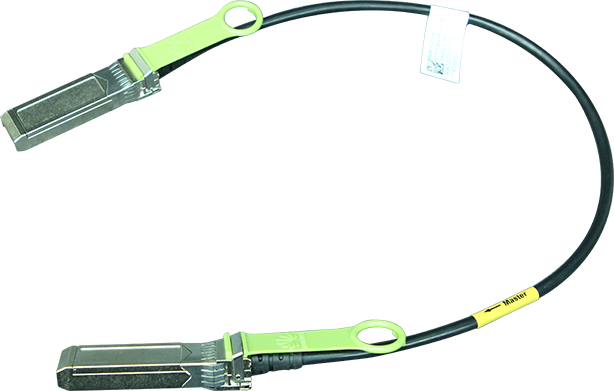
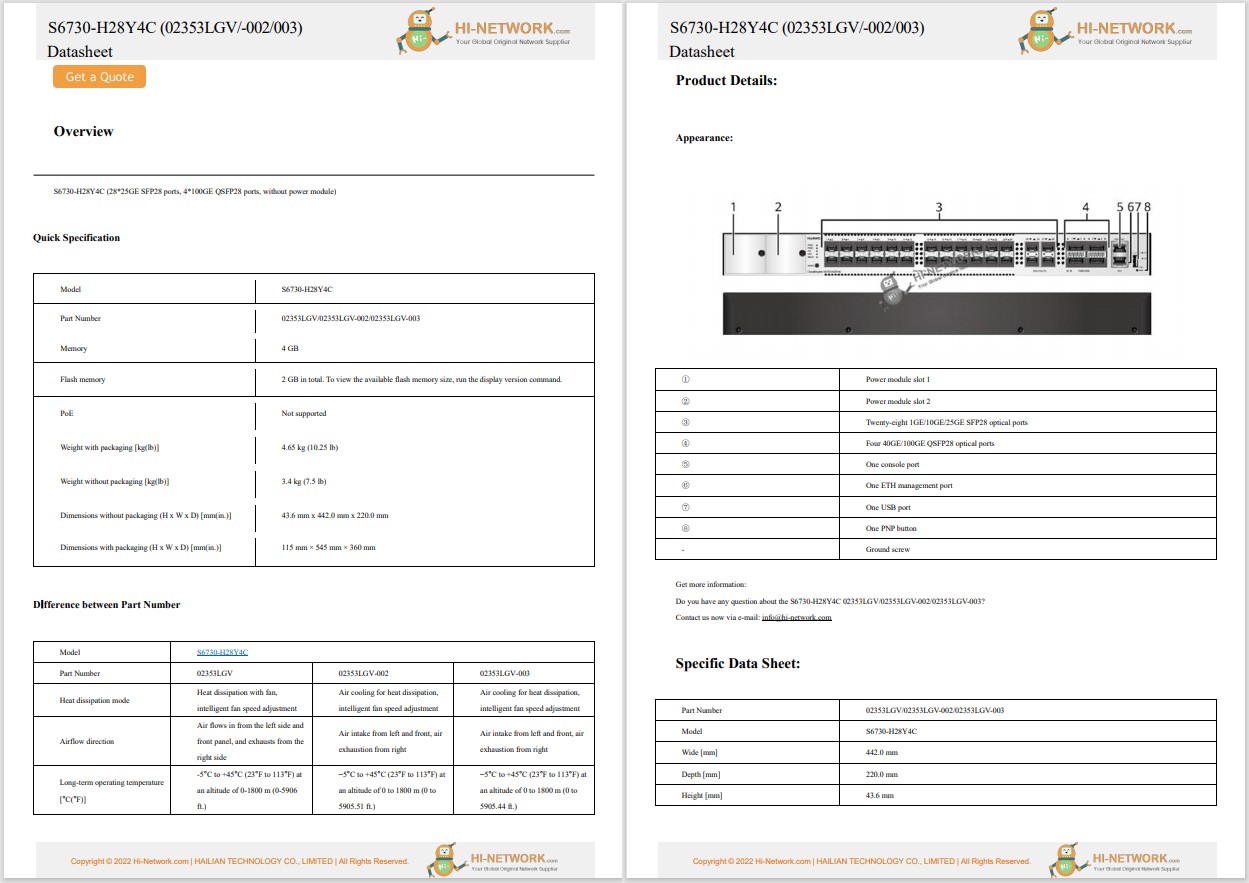
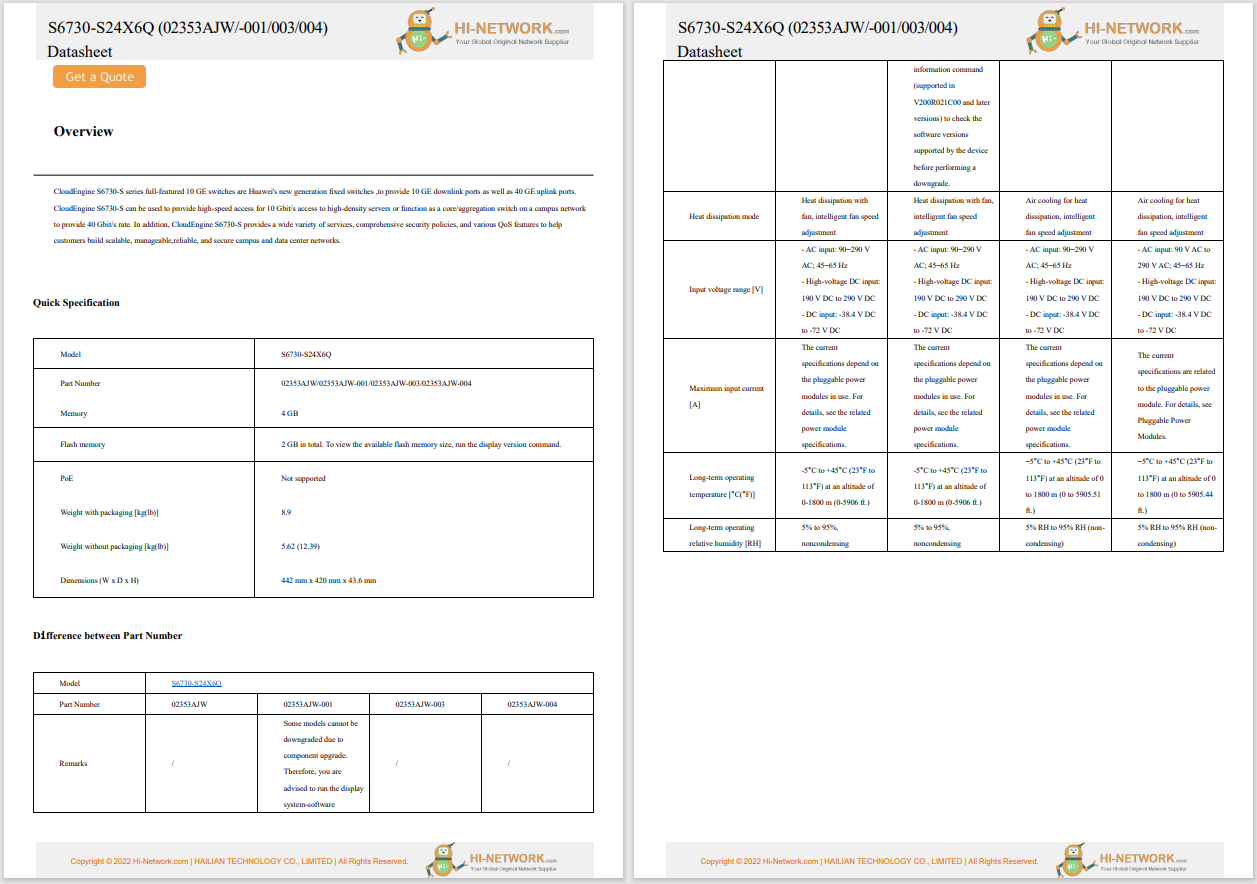
Cisco Wireless AP and Controllers
For Cisco product list and quote, please visit: https://www.hi-network.com/categories/cisco or contact us at www.hi-network.com (Email: [email protected])
 Hot Tags :
hot products
Hot Tags :
hot products