







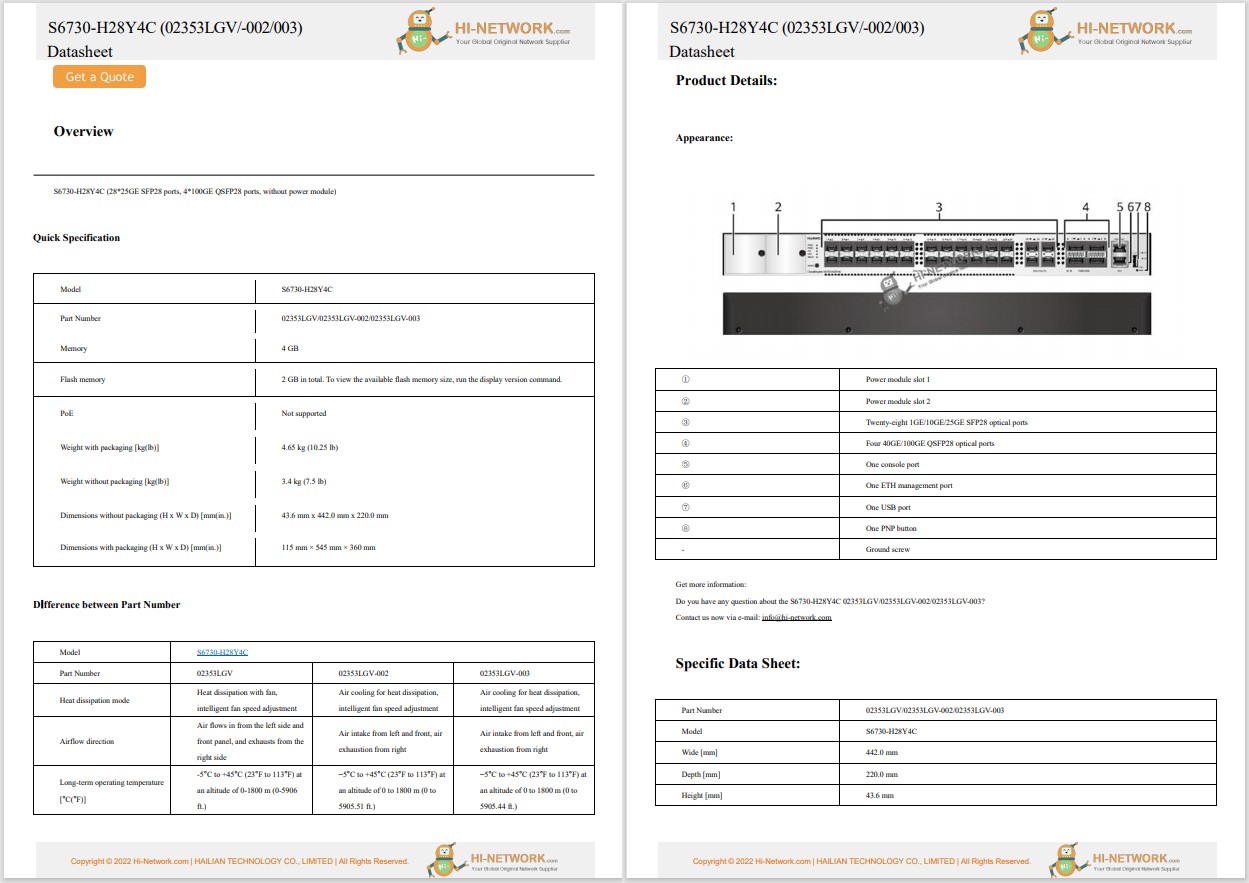


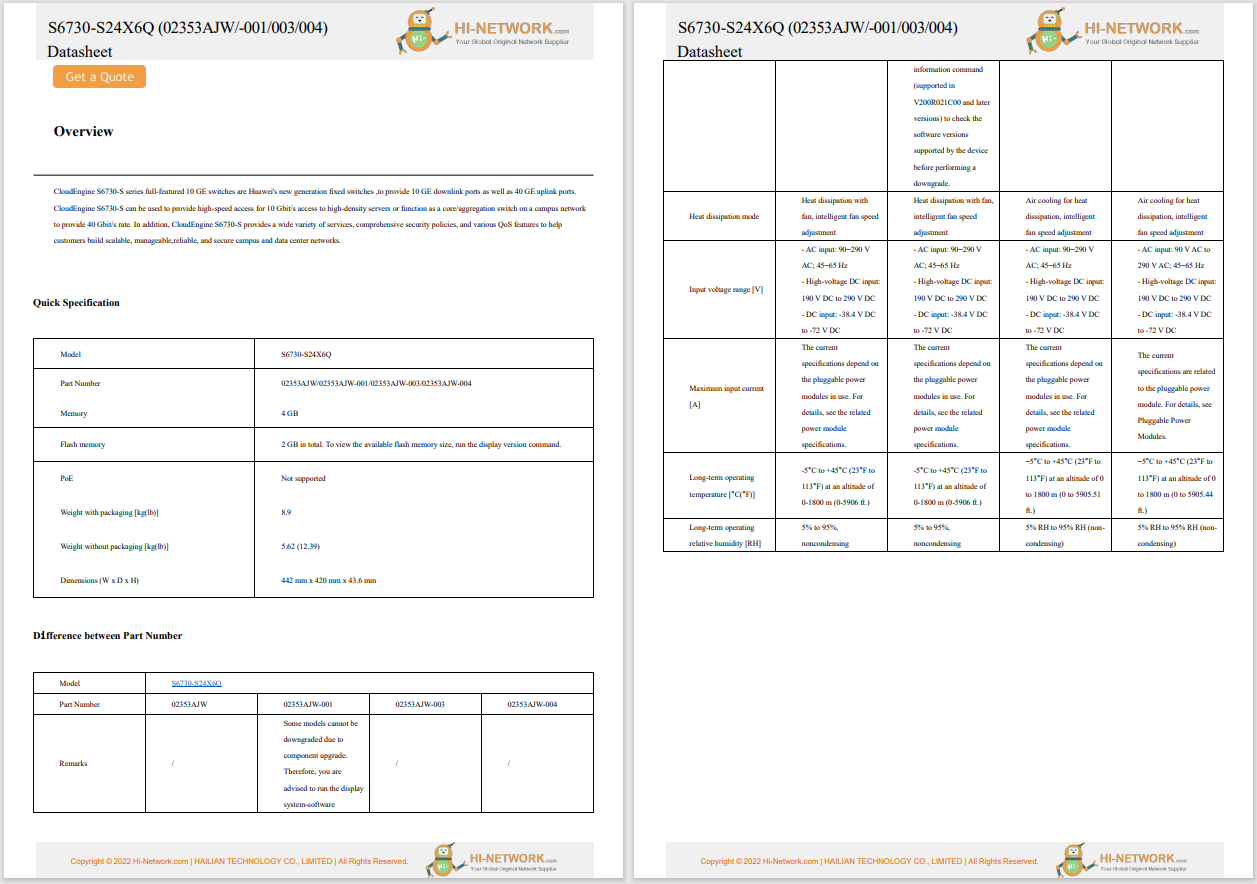
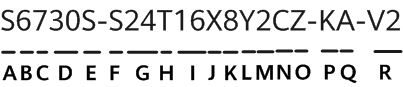

















China's chipmaking equipment purchases are expected to decline in 2025, following three years of growth, due to overcapacity and increasing restrictions from US sanctions. After purchasing$41 billion in equipment in 2024, which accounted for 40% of global sales, China's spending is predicted to fall by 6% to$38 billion this year, marking the first decline since 2021. The drop in demand is attributed to reduced purchases in response to export controls and an excess of manufacturing capacity.
Despite these challenges, China has been a key driver for the global wafer fabrication equipment market over the past few years, even as other sectors saw downturns. Much of China's equipment buying has been linked to stockpiling efforts in response to US sanctions aimed at limiting China's ability to produce advanced chips, particularly for military use. Chinese firms, like SMIC and Huawei, have continued to advance in chip production, although at a higher cost and with more effort, while also focusing on expanding in the mature-node chip market.
In addition to growing its domestic production capabilities, China's leading equipment manufacturers, such as Naura Technology Group and AMEC, are expanding internationally. However, the country still faces significant challenges in self-sufficiency, particularly in areas like lithography systems, testing, and assembly tools. While China's domestic companies have made strides in equipment sales, they still rely heavily on foreign suppliers for advanced technology in these areas.
 Hot Tags :
Capacity development
Critical infrastructure
Semiconductors
Hot Tags :
Capacity development
Critical infrastructure
Semiconductors