









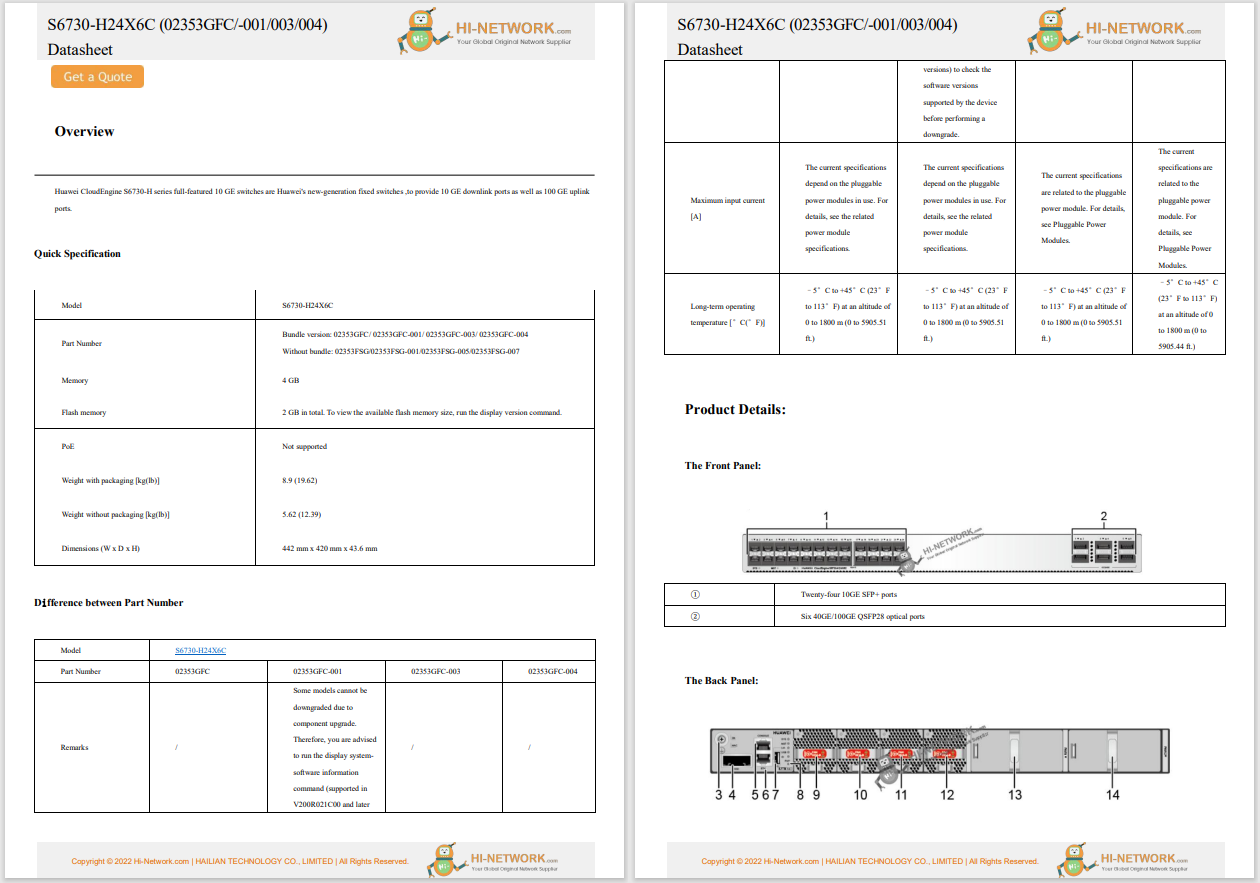
















This post was authored by Nick Biasini
On January 27th, Talos researchers began observing a new Angler Exploit Kit (EK) campaign using new variants associated with (CVE-2015-0311). Based on our telemetry data the campaign lasted from January 26th until January 30th with the majority of the events occurring on January 28th & 29th.

Researchers detected the new campaign when referencing a known hash that was delivering the recent Flash 0-day (CVE-2015-0311). During this investigation several layers of subdomains are being used to avoid detection. As of the writing of this blog ~1800 domains have been seen being used by the following IP addresses:
These domains are associated with the landing page and exploits. None of the actual root domains appear to be compromised and are legitimately registered to owners. It appears that the actors have managed to compromise a large group of registrant accounts and have set up subdomains (i.e. acfbbfhdahfeh.legitdomain.info). There are enough of these domains that some of them are only seen once before being abandoned. The majority of the compromised domains are registered through GoDaddy and it appears that 50+ accounts have been compromised. Many of these accounts control multiple domains with some controlling 45+ unique domains. Below is a sample showing a small portion of the subdomains that were registered to a single domain all resolving to a single IP address.

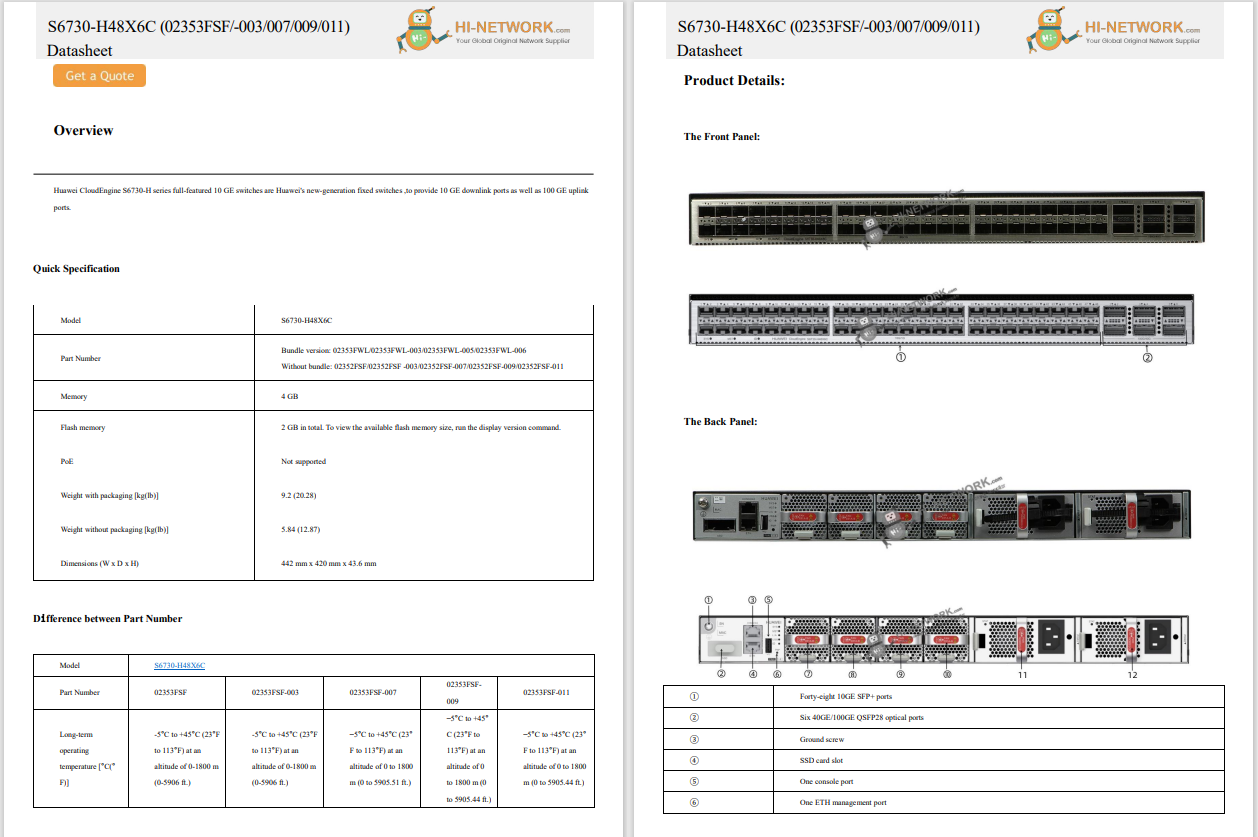
To take the approach a step further these actors have utilized another tier of the subdomains to serve as the initial redirection page. Our telemetry data points to another ~650 of these subdomains linked back to a single IP address,176.103.144.48. The main distribution method is malvertising with the malicious advertisement pointing to an initial tier of compromised subdomains. These sites then redirect to another subdomain delivering landing page and exploitation. These actors have been seen serving both Adobe Flash and Silverlight exploits, which will be discussed in more detail below.
 Click Image to Enlarge
Click Image to EnlargeExploit Details
The exploits that are being served are a combination of known and new variants of existing vulnerabilities. The first and most commonly served sample:
SHA256:56f61bd84f6851dcd749c95ebcbc94b7814bedb12ae72db776e3c27d4be43ef8
is the widely distributed version of the Flash 0-day for Angler Exploit Kit (details). The second groups of samples were Silverlight based, which are known to be part of the Angler EK, as Talos has discussed previously.
SHA256:ca0cd15e28620dcb1b2fb5d29fb6daaa88346d8775139607bd9d2f583415e7b8
There is an additional group of hashes that are all variants of CVE-2015-0311 but have very low detection rates currently (Between 1/57 -3/57)
SHA256:6e2d96990f92864c81277ed3291d79c27e0c326df43eccb050058cc3b1705ade
SHA256:003156c92d99aa8bca0f7bc443a03f32a8ce5e26e940f6681747abbc44e1409c
Despite the low Anti-Virus detection rates, Cisco AMP and Network Security IDS & NGFW successfully detected and blocked the new variants as well as the older samples.
IOCs
IP Address:
85.25.107.126
207.182.149.14
178.32.131.248
178.32.131.185
85.25.107.127
176.103.144.48
SHA256:
56f61bd84f6851dcd749c95ebcbc94b7814bedb12ae72db776e3c27d4be43ef8
6e2d96990f92864c81277ed3291d79c27e0c326df43eccb050058cc3b1705ade
003156c92d99aa8bca0f7bc443a03f32a8ce5e26e940f6681747abbc44e1409c
ca0cd15e28620dcb1b2fb5d29fb6daaa88346d8775139607bd9d2f583415e7b8
Domain list
Conclusion
This is another example of how Angler Exploit Kit continues to differentiate itself. It changes and evolves on a constant basis producing new variation on the existing exploits as well as providing enough customization on the recent vulnerability (CVE-2015-0311) to effectively avoid reliable detection. If the first month of 2015 is any indication, the Angler Exploit Kit could have a big year.
Snort Rules: 33271-33274, 33286 for the most up to date list please refer to Defense Center

Advanced Malware Protection (AMP) is ideally suited to prevent the execution of the malware used by these threat actors.
CWS or WSA web scanning prevents access to malicious websites, including the downloading of the malware downloaded during these attacks.
The Network Security protection of IPS and NGFW have up-to-date signatures to detect malicious network activity by threat actors.
 Hot Tags :
Cisco Talos
Talos
0-day
angler
flash
exploit kit
Hot Tags :
Cisco Talos
Talos
0-day
angler
flash
exploit kit