



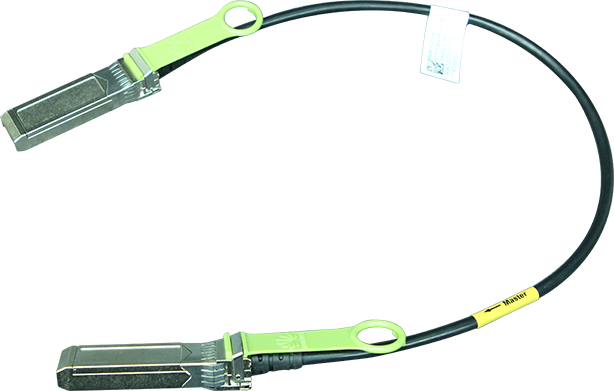




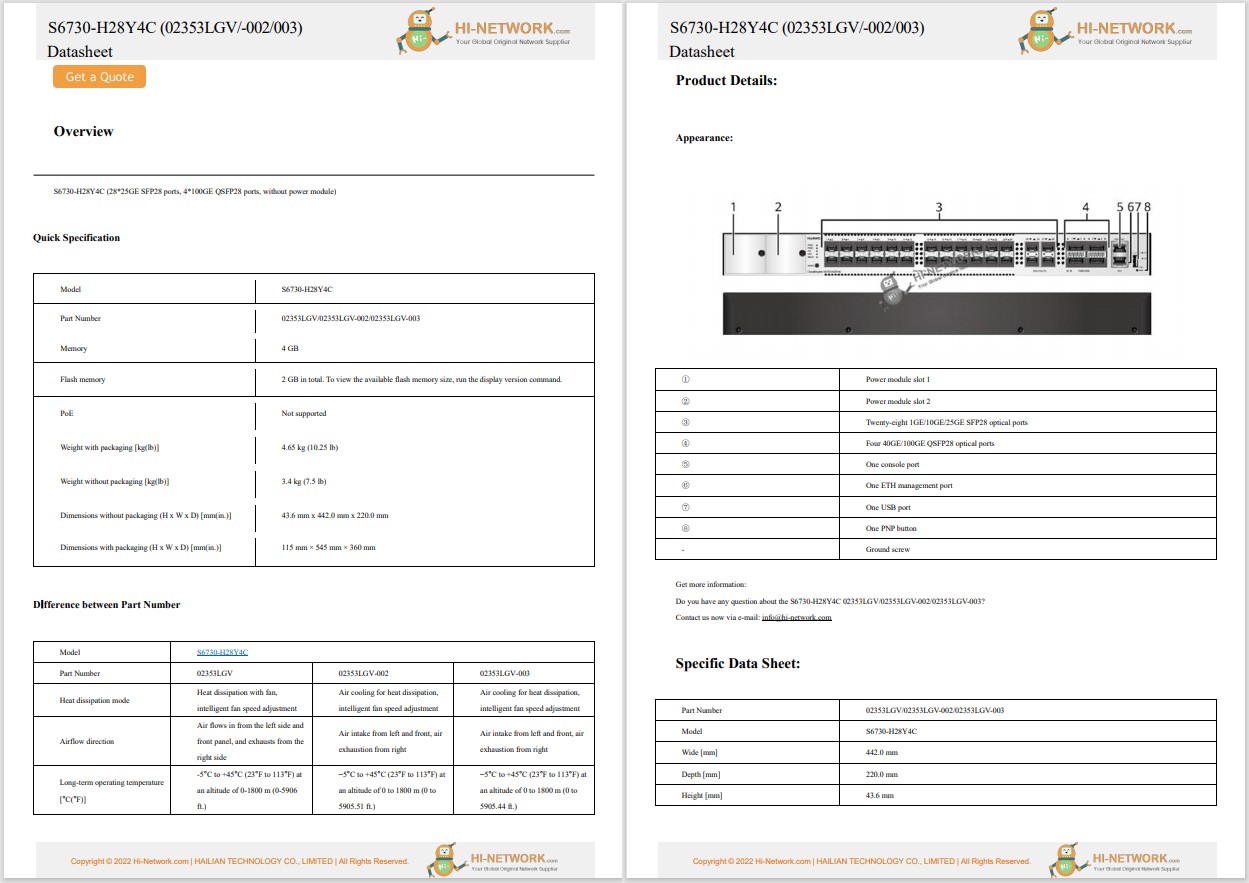


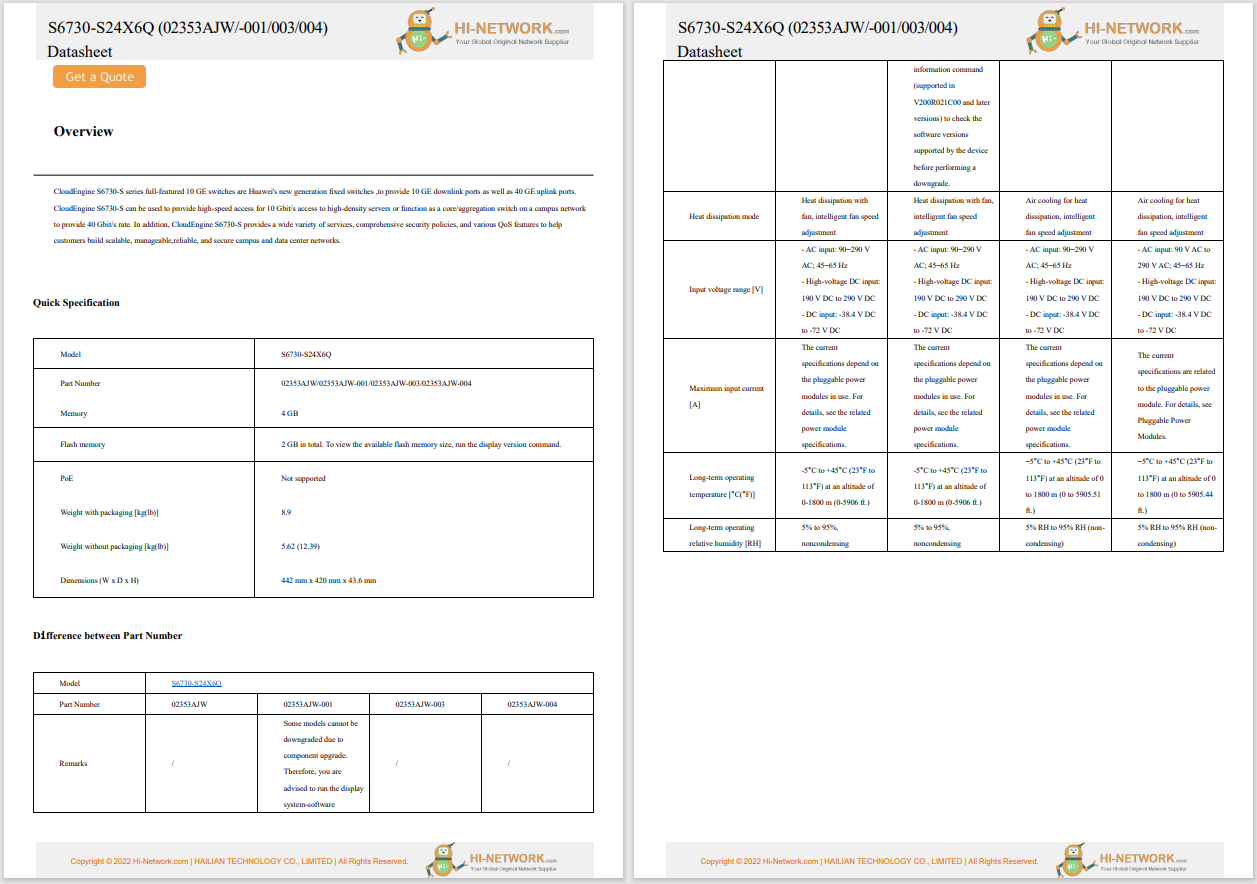
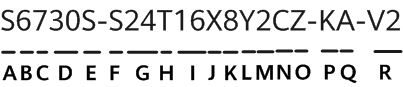
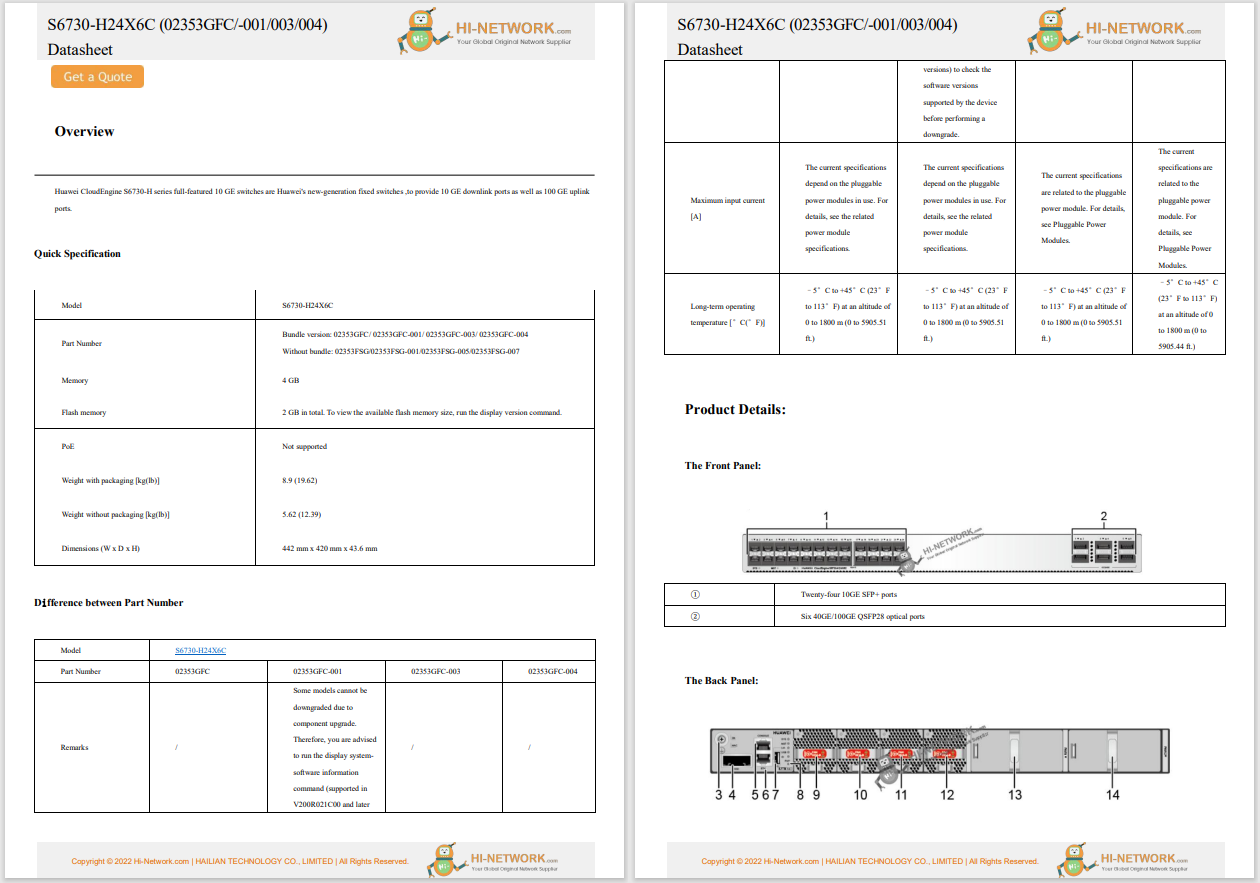

















I have 2 Gigabits per second (Gbps) of fiber internet in my home for$120 a month. I'm lucky. I have access to that kind of broadband and the money to pay for it. Many people aren't that fortunate.
On Wednesday,May 1,the Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP),a critical initiative to provide affordable broadband, ran out of money. That means 23 million households -- roughly 60 million Americans -- will have to choose between paying for internet or paying for food, rent, andother utilities.
Also: The FCC restores net neutrality - here's what it means for the internet
Once upon a time, internet access was a luxury. Today, it's a necessity. We use it to do our jobs, see our doctors, and send our kids to school. And for millions of US citizens, mainly older adults, military veterans, Indigenous communities, people living in the country, and low-income, working families, the internet just became more expensive.
In my ancestral home of Calhoun County, West Virginia, one of the country's least-connected states, over half the population was eligible for ACP. My friends and family who still live there tend to be older and less well-employed. With a population of just over 6,000 people, it's as rural as rural gets. Forget broadband: I still have at least one friend there who's connected to the internet via a dial-up modem (yes, it still exists).
Now, many of them will be facing higher internet bills. It may not sound like much. The ACP only provided a monthly consumer benefit of$30 -- up to$75 for those on qualifying Tribal lands -- to eligible households so they could afford high-speed internet services. But when you're poor, as I was raised,$30 is real money.
The ACP is a political rarity: a policy that most Congress members support. According to a 2023 Public Opinion Strategies and RG Strategies poll, 78% of voters support the ACP, including 64% of Republicans, 70% of independents, and 95% of Democrats.
Unfortunately, even though the bipartisan Affordable Connectivity Program Extension Act of 2024 (H.R. 6929 and S. 3565) was introduced in Congress in January, both bills have gone nowhere.
Also: How to see if your internet provider is overcharging you (or delivering slower speeds)
Both proposals make solid financial sense. The politically neutral Benton Institute for Broadband and Society estimates that the ACP generates$16.2 billion per year in employment income and time saved, which is twice its annual cost. Other research shows the financial benefits could go even further. As Brookings Fellow Blair Levin put it, a February paper estimates that "for every dollar spent on the ACP, the nation's GDP increases by$3.89."
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Chairperson Jessica Rosenworcel wrote in a last-ditch appeal to Congress that "additional funding from Congress is the only near-term solution for keeping the ACP going. If additional funding is not promptly appropriated, the one in six households nationwide that rely on this program will face rising bills and increasing disconnection." She concluded that "time is running out."
So why hasn't Congress moved? Some senior Republican Senators and Representatives say the ACP is just part of the "Biden administration's reckless spending spree" and that it's "speculative to claim that 25 million households will lose broadband if the ACP does not get new funding."
In other words, it's politics.
So, what can you do in the meantime?
First, look for less expensive internet plans. Slow internet is still better than no internet.
You should also check to see if your internet service provider (ISP) offers a low-income discount plan.AT&T , Cox , Optimum , Spectrum , and Xfinity , among others, offer inexpensive packages.
If your ISP doesn't, checkEveryone On's provider search page for a new, low-price ISP.
There's also another Federal program called Lifeline. For low-income households, it offers a$9.25 monthly subsidy that can be used for home internet service. Unlike the ACP, it's permanently funded, so you won't have to worry about losing it. You can qualify if your income is 135% or less than the federal poverty guidelines or if you participate in SNAP, Medicaid, or other federal poverty programs. Check the Universal Service Fund to see who offers Lifeline services in your area.
Also: The best business internet providers of 2024
The non-profit e-waste reclaiming organization Human-I-T also offers low-cost devices and internet services, like this 4G-based option that costs$15 a month. It's only available for people under approved government assistance programs such as SNAP, SSI, or Section 8 Housing, or who have an annual household income within 200% of the Federal poverty level.
A blast from the past, the old-school NetZero ISP still offers a free, albeit very limited, dial-up plan. When I say limited, I mean 10 hours a month of connectivity. Another low-cost service, FreedomPop, offers 5G services for as little as$10 a month. It only comes with 1 Gigabyte of traffic a month, but it's hard to beat for that price.
You may also be able to cut your ISP bill by buying your own equipment. Many charge around$10 monthly to rent equipment such as cable modems and Wi-Fi access points. You can find new Wi-Fi routers for as little as$50, but really almost any Wi-Fi router you can find should be all you need. You can also check out second-hand stores -- I've found great hardware that way that was worth far more than I paid for it.
Modems are a different story. You usually need one of a handful of specific models to work with your ISP service. Once you've found out which will work for you, you can usually buy one. Yes, it will cost you a pretty penny upfront, but you can likely recoup the price in a year.
You can also try haggling with your ISP. If your ISP customer service representative has a choice between losing you as a customer or offering you a lower price, they may give you a better deal. You never know until you try; it's worked for me over the years.
Also: 6 ways to save money on TV streaming without losing the shows you love
If you're struggling to choose between cable TV and the internet, see what bundles your providers offer. Many offer discounted TV/internet packages. You may also be better off with a second-tier ISP/cable provider. CheckHighSpeedInternet's TV and internet bundle page for offers as low as$40 a month. Fair warning: Most such plans cost a good deal more.
You probably already know that almost all libraries offer free Wi-Fi. What you may not know is that many also let you borrow a cellular Wi-Fi hotspot. Typically, you can borrow a unit for two weeks, and they come with free connectivity. Most, but not all, use the T-Mobile network, but you don't need a T-Mobile account to use them.
Of course, in the best-case scenario, Congress will eventually reauthorize ACP. But I'm not holding my breath.
 Hot Tags :
Home & Office
Networking
Broadband
Hot Tags :
Home & Office
Networking
Broadband