



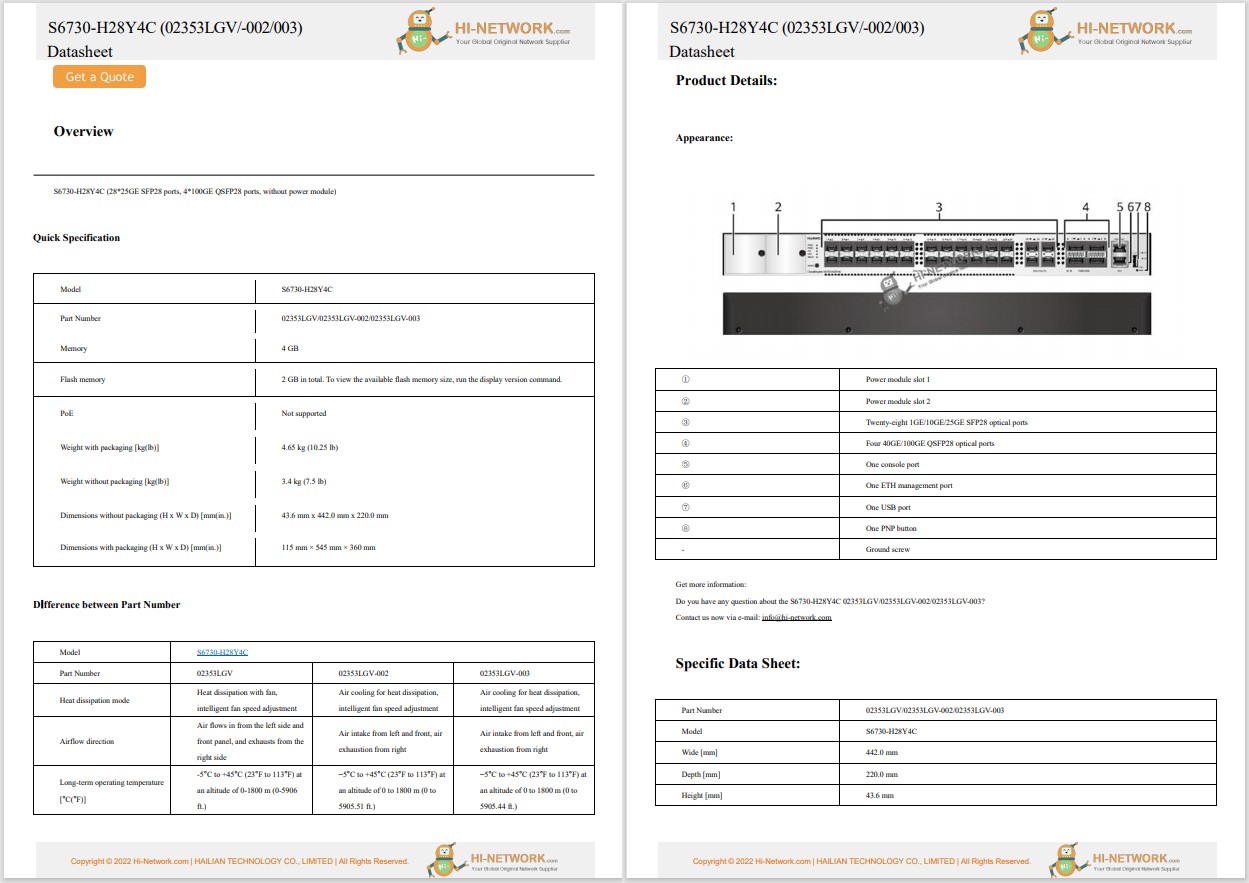


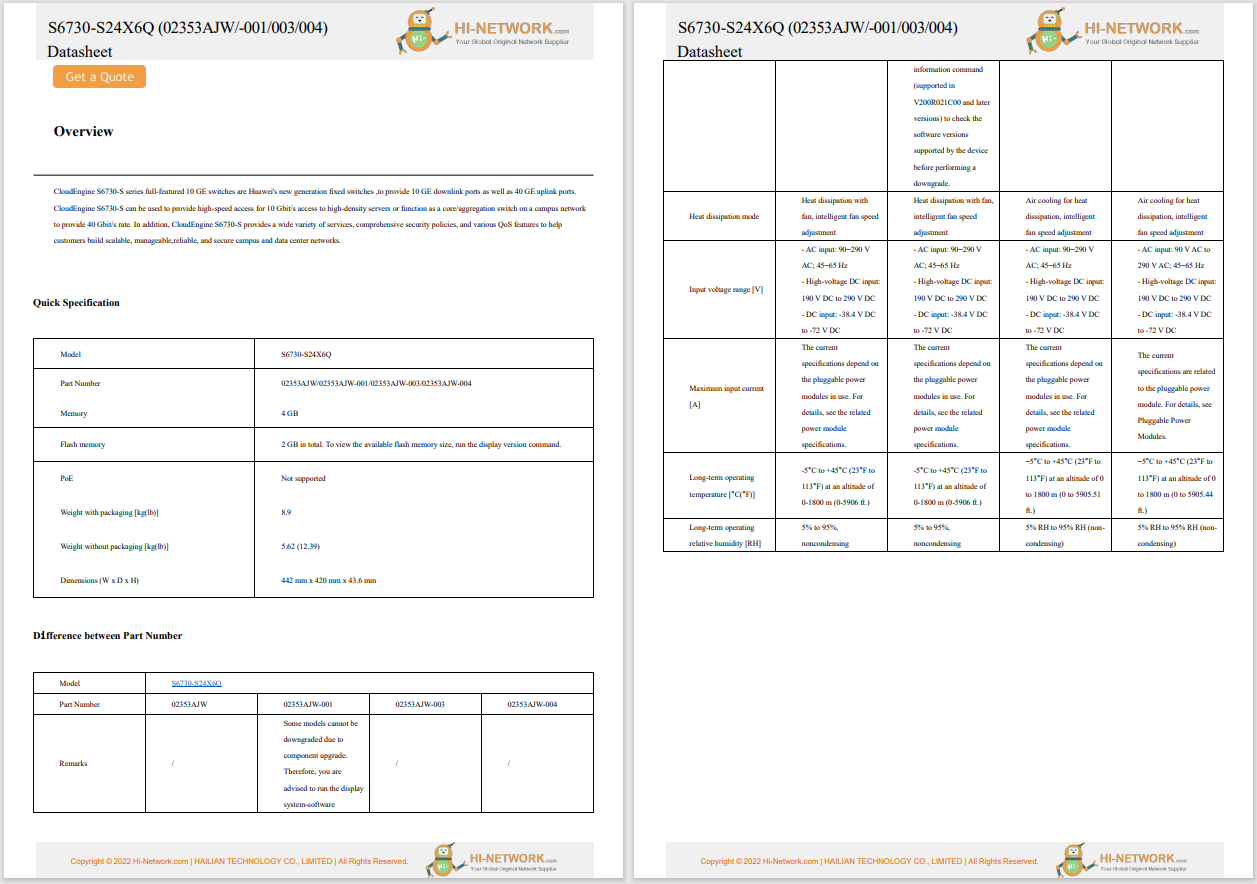
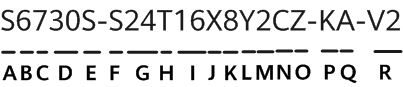
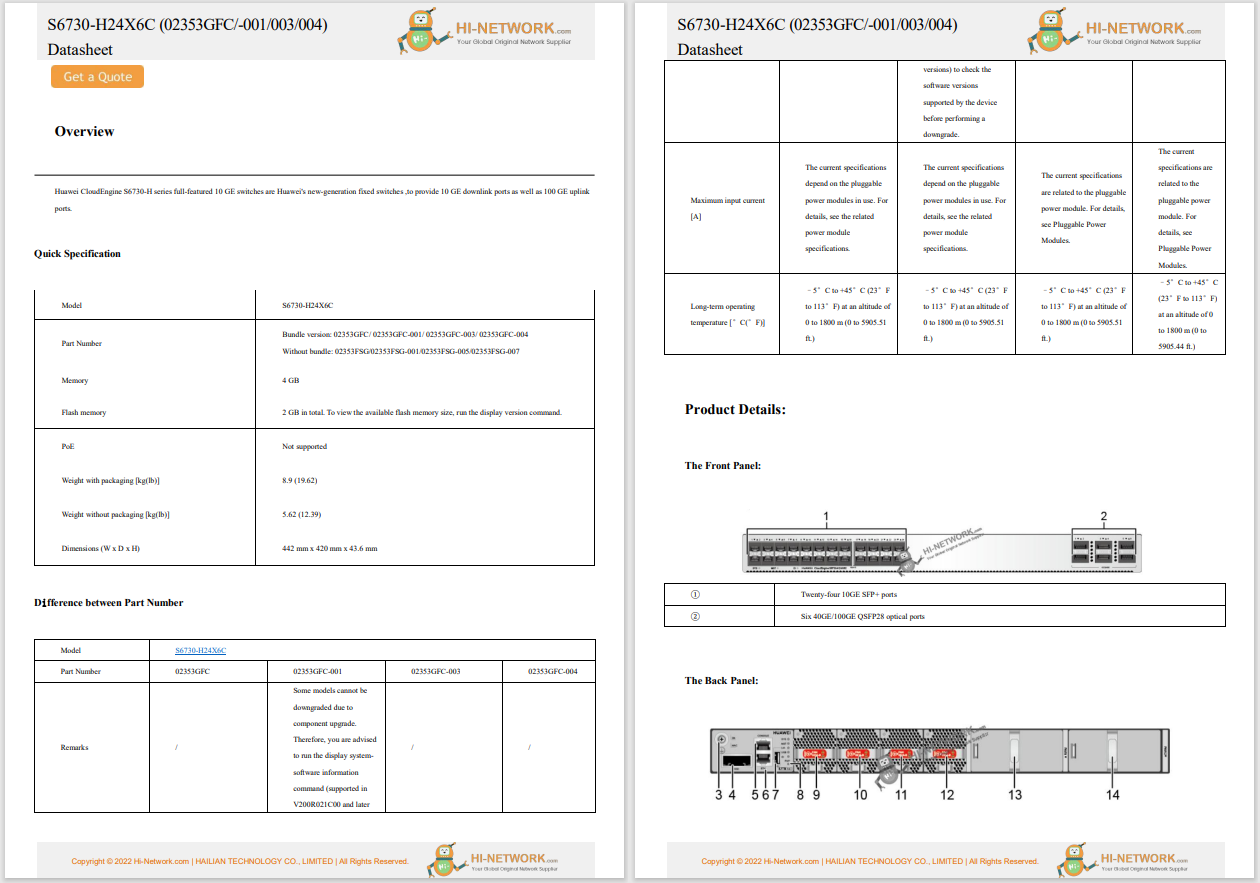




















In the context of escalating tensions between the US and China, Chinese corporations, including Huawei and Tencent, have notably expanded their global patent portfolios within the cybersecurity technology domain. A report from Nikkei Asia reveals that Chinese companies secured six out of the top 10 positions in terms of global cybersecurity patent holdings as of August. This data, compiled in cooperation with LexisNexis, encompassed patents registered across 95 countries and regions.
IBM claimed the top spot with 6,363 patents, closely followed by Huawei with 5,735 and Tencent with 4,803 patents. Other Chinese enterprises, such as Ant Group, Alibaba Group Holding, and China Investment Corp., also achieved prominent rankings.
Why does this matter?
These developments mirror China's strategic drive to attain self-sufficiency in technology and reduce reliance on foreign innovations, particularly in light of US restrictions and export controls. Notably, Huawei has been a focal point of US sanctions aimed at safeguarding American networks and supply chains. The surge in patent filings by Chinese firms underscores the increasing significance of protecting intellectual property in the global competition for technology and data supremacy.
 Hot Tags :
Cybersecurity
Intellectual property rights
Hot Tags :
Cybersecurity
Intellectual property rights