


























ChatGPT is an artificial intelligence chatbot that has helped kickstart a whole new AI industry, with lots of competition from Google Gemini, Microsoft Copilot, Meta's Llama 3, and Anthropic's Claude, among others. This article will tell you what "GPT" stands for and what it tells you about the AI platform.
The "GPT" in "ChatGPT" stands for Generative Pre-trained Transformer:
However, the developer of ChatGPT, OpenAI, also uses the term "GPT" for the names of the language models that ChatGPT runs on.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/19-ways-to-fix-a-chatgpt-network-error-on-long-responses-2c22dc8a46b540f28f81dfafb452492f.jpg)
CreativeDJ/E+/GettyImages
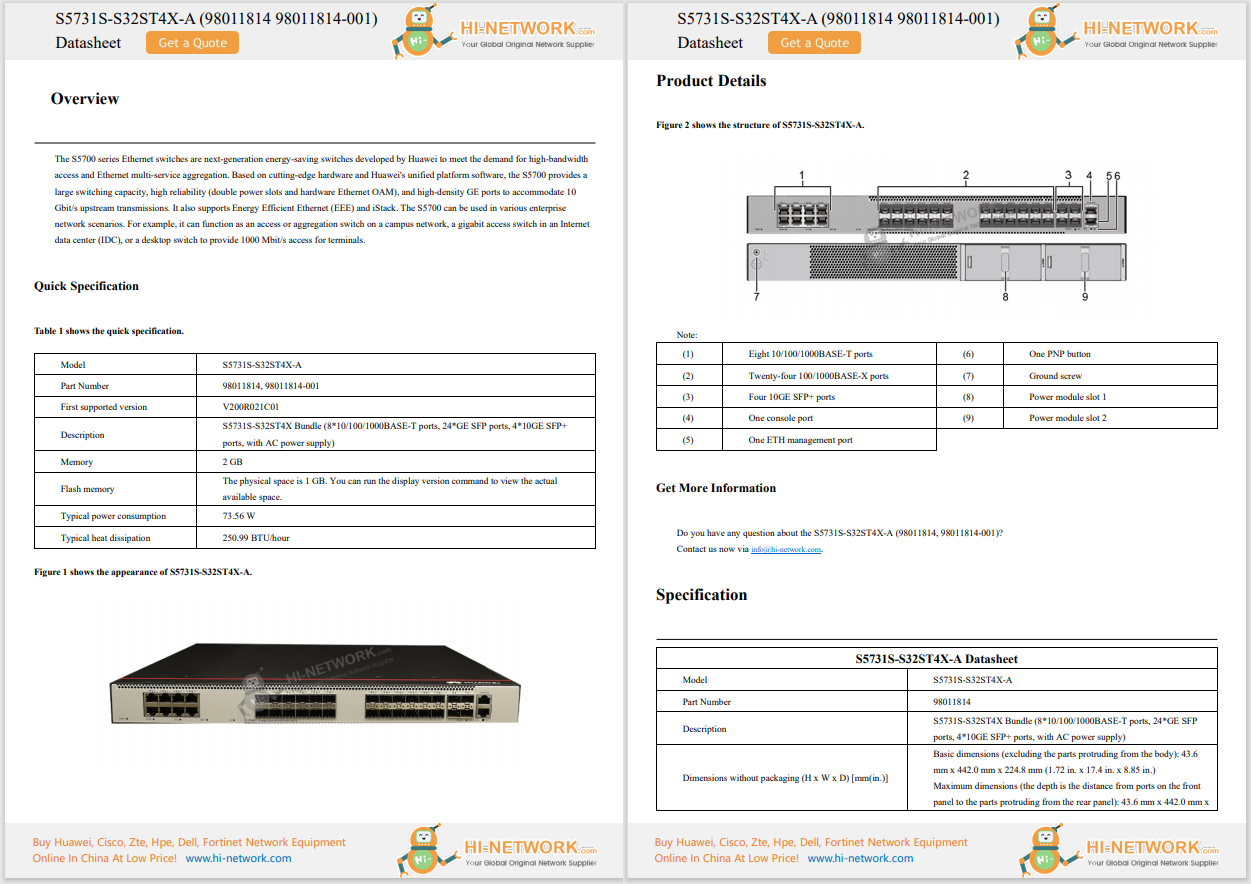
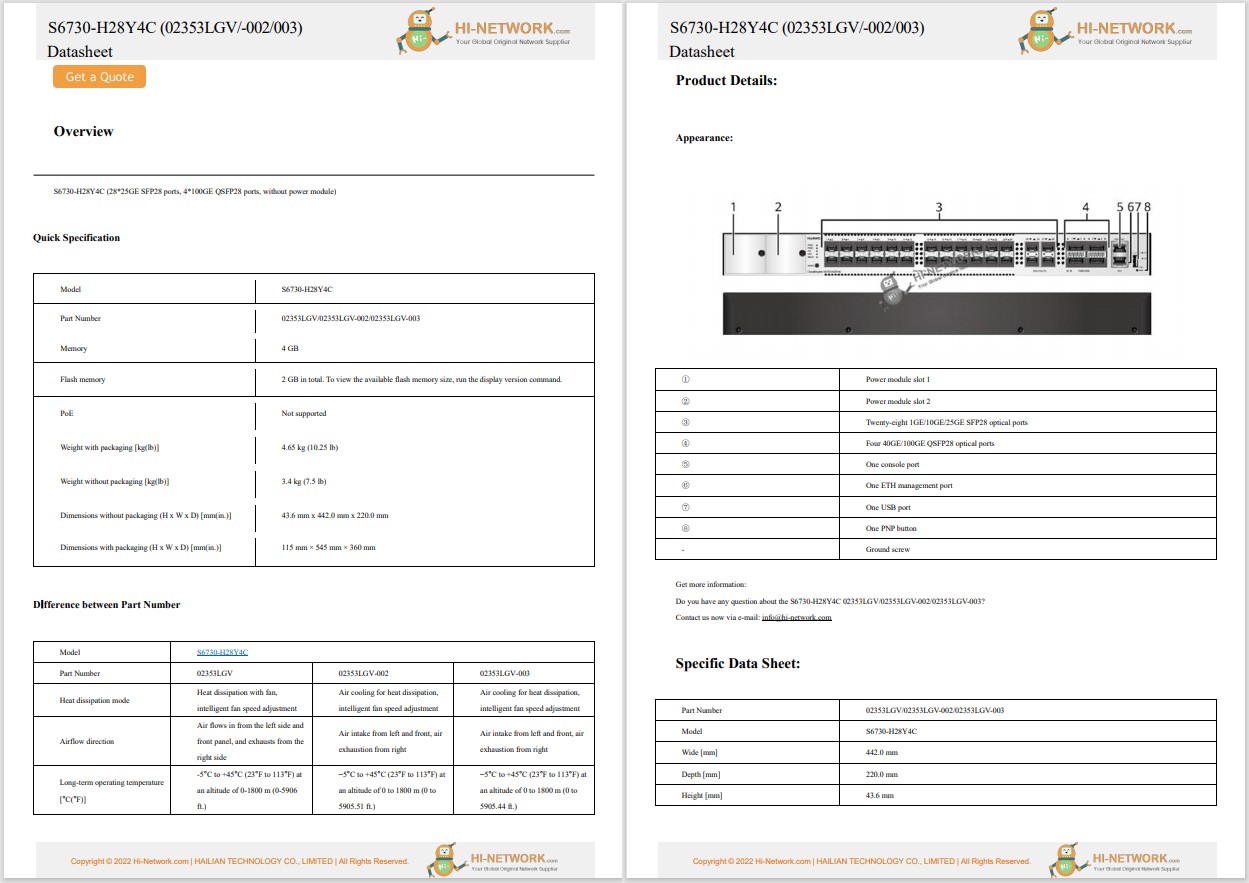
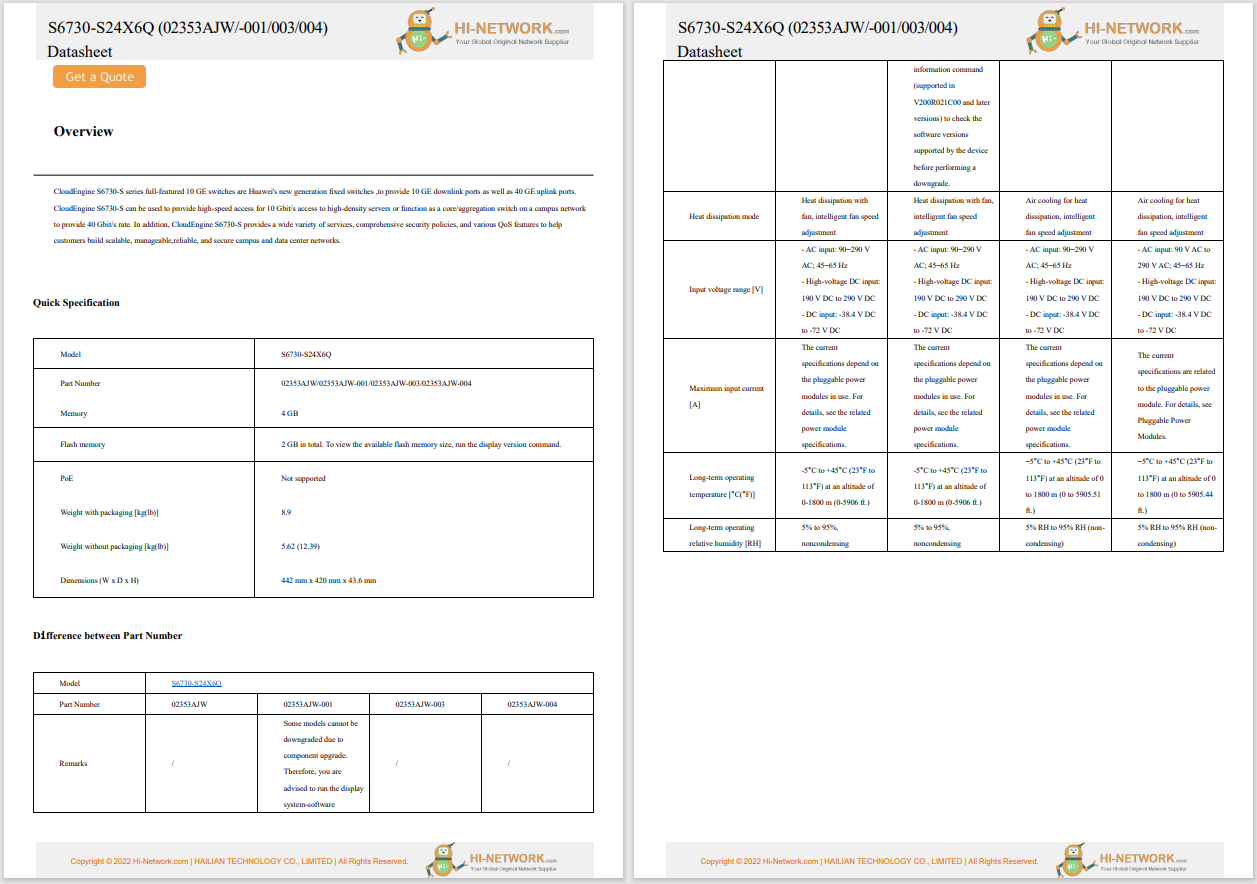
When ChatGPT debuted in 2022, it launched with the GPT-3 language model, which at the time was the most advanced publicly available. It was trained on 175 billion parameters (pieces of data) that the AI uses to weigh its responses and help it do so in a manner that is understandable for humans. It used training data up to 2020, and it had the ability to interact with text.
The GPT-3.5 language model, which launched in 2023, used slightly more parameters for training and included training data up until 2021 so it could respond to more queries. It was also far faster in its responses and has remained the main model available for free ChatGPT users to this day.
2023's GPT-4 expanded its parameters further (to an undisclosed amount) and added training data up until 2022. It also extended the context length so it could retain the information you'd shared with it throughout a conversation more readily. It also added basic image-generation capabilities.
GPT-4o, which launched in 2024, expands context length even further, improves training data up to 2023, and features much more advanced multi-modal features, like image generation, audio processing, and improved accuracy of its responses.
ChatGPT is a type of generative AI that can respond with human-like text, images, audio, or video, all created by the AI. It isn't programmed to respond in a certain way. It's programmed to learn from the data, and then the AI itself decides how to respond to the prompts it's given.
This method is different from a more traditional, rule-based AI, which uses predefined rules and logic to make decisions and only works in limited scenarios where the input can be expected.
 Hot Tags :
Smart & Connected Life
Hot Tags :
Smart & Connected Life